Understanding Meloxicam: A Prescription Pain Reliever
What is meloxicam? Meloxicam is a prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve pain, swelling, and inflammation caused by arthritis and other conditions. Here’s what you need to know:
- Drug Class: NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug)
- Primary Uses: Treats osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- How It Works: Blocks enzymes that cause pain and inflammation in the body
- Common Brand Names: Mobic, Vivlodex, Qmiiz
- Prescription Status: Requires a doctor’s prescription
- Key Fact: In 2023, meloxicam was the 27th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 20 million prescriptions filled
Important Warning: Meloxicam carries serious risks, including an increased chance of heart attack, stroke, and stomach bleeding. It should be used at the lowest effective dose for the shortest time needed.
Meloxicam is not an opioid and is not considered addictive, but some people with chronic pain may misuse it by taking more than prescribed. Understanding its function, risks, and safe use is crucial for anyone prescribed this medication.
At Addiction Helpline America, we provide confidential support for prescription medication concerns, including information about what is meloxicam and safe pain management alternatives. We connect people with treatment options and educational resources to support informed healthcare decisions.

Similar topics to what is meloxicam:
What is Meloxicam and How Does It Work?
Meloxicam is a prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) from the oxicam family. It’s chemically related to other NSAIDs like piroxicam and is commonly prescribed for arthritis pain and inflammation.
Unlike over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen, meloxicam requires a prescription. It’s a more potent medication for the long-term management of chronic conditions, not for minor aches.
Think of inflammation as a faulty fire alarm causing ongoing pain. Meloxicam helps turn down that alarm, improving comfort and daily function.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
How meloxicam reduces pain and inflammation
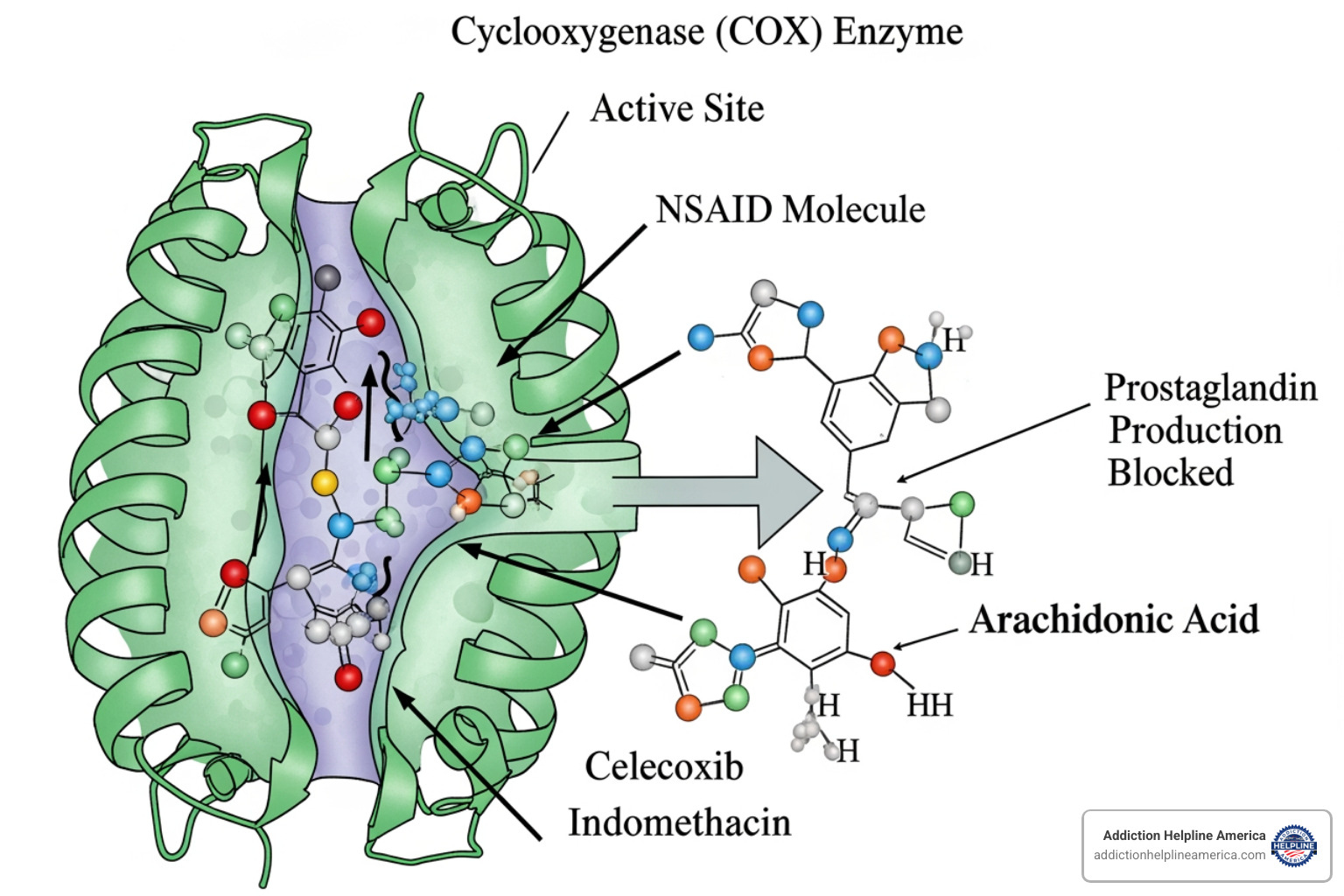
Meloxicam works by targeting enzymes called cyclooxygenase (COX). These enzymes create prostaglandins, which are chemical messengers that trigger inflammation, pain signals, and fever.
When you have an inflammatory condition like arthritis, your body overproduces prostaglandins. Meloxicam blocks the COX enzymes, stopping excess prostaglandin production. This results in less pain, swelling, stiffness, and fever.
There are two types of COX enzymes: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 protects the stomach lining, while COX-2 is primarily responsible for inflammation and pain. Meloxicam is a preferential COX-2 inhibitor, meaning at lower doses, it targets COX-2 more than COX-1. This was thought to cause fewer stomach problems, though higher doses can still affect COX-1.
A key feature is its long-acting relief, typically requiring only one dose per day. This makes it convenient for chronic arthritis but not suitable for immediate pain relief, as it takes several days to reach full effectiveness. It’s designed for steady control of ongoing inflammation.
More about meloxicam’s properties
What is meloxicam used to treat?
Doctors prescribe meloxicam primarily for different types of arthritis. The most common is osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears down, causing bone-on-bone pain. Meloxicam helps reduce these symptoms and improves movement.
Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease where the body attacks joint linings, is another major use. Meloxicam helps manage the pain and swelling, though it doesn’t alter the underlying disease.
For children aged 2 and older, meloxicam can treat juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA), helping relieve joint pain and inflammation.
Meloxicam also helps with ankylosing spondylitis, a type of arthritis affecting the spine, by improving mobility and reducing discomfort.
More recently, an intravenous (IV) form of meloxicam (Anjeso, Xifyrm) was approved for post-operative pain management. This IV version can be used alone or with other non-NSAID pain medications, offering a non-opioid option for surgical pain and potentially reducing the need for addictive medications. Some medical teams combine it with local anesthetics for better pain control.
At Addiction Helpline America, we understand that managing chronic pain safely is crucial, and knowing what is meloxicam and how it fits into your treatment plan is an important part of that journey.
Important Side Effects and Safety Warnings
While meloxicam is effective for chronic pain, it’s crucial to understand its potential dangers. These risks are as important to know as its benefits.
Serious Cardiovascular and Gastrointestinal Risks
Meloxicam has an FDA Black Box Warning, the most serious alert, to ensure you and your doctor make an informed decision. The warning covers two main risks.
First, cardiovascular risks: NSAIDs like meloxicam (except aspirin) increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke. This risk can appear within weeks of use and grows with longer use or higher doses, especially for those with existing heart conditions. Meloxicam can also cause or worsen high blood pressure and may increase heart failure risk.
Second, gastrointestinal risks: Meloxicam can cause serious digestive issues like stomach ulcers, internal bleeding, and perforation (a hole in the stomach or intestines). These can occur without warning and may be fatal.
Your risk of stomach problems is higher for older adults, those with a history of ulcers or GI bleeding, those in poor health, and those who drink or smoke. This is why the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration is recommended.

Some symptoms require immediate medical attention—don’t wait if you experience:
- Chest pain, especially if it spreads to your arm or jaw
- Sudden numbness or weakness on one side of your body
- Sudden severe headache, slurred speech, or vision changes
- Shortness of breath, even with light activity
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, or hands
- Black, bloody, or tarry stools
- Vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds
- Severe stomach pain
- Unexplained weight gain
If any of these happen, call your doctor or get emergency help. Don’t take another dose until you’ve talked with a healthcare professional. Your pharmacist should give you a Medication Guide; you can also find information at the FDA Medication Guide website.
What is meloxicam’s risk to your stomach?
Beyond the most serious GI complications, meloxicam can cause uncomfortable stomach side effects. Many people experience stomach pain, discomfort, heartburn, or nausea.
More seriously, black or bloody stools or vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds are signs of internal bleeding and require immediate medical attention.
Taking meloxicam with food or milk may reduce mild stomach upset. If symptoms persist or worsen, talk to your doctor.
Common, Less Severe Side Effects
It’s also important to know the common, less severe side effects. These include diarrhea, constipation, indigestion, gas, headaches, and dizziness or drowsiness. Be cautious when driving or operating machinery.
Other common effects are ringing in your ears (tinnitus), a mild rash or itching, swelling (especially in the ankles, feet, or legs), and cold-like symptoms like a runny nose or sore throat.
While not usually emergencies, contact your doctor or pharmacist if these side effects persist, worsen, or become bothersome, as your treatment may need adjustment. Other side effects are possible, so communicate openly with your healthcare provider. In the U.S., you can report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch or by calling 1-800-FDA-1088.
Dosage, Administration, and Safe Handling
To use meloxicam safely, take it exactly as prescribed. Do not take extra doses for pain flare-ups, as this significantly increases your risk of serious side effects like heart attack, stroke, or stomach bleeding without providing better relief.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Recommended Dosages and Forms
Meloxicam comes in several forms. Oral tablets (7.5 mg and 15 mg) are most common and taken once daily. An oral suspension (liquid) is available for those who have trouble swallowing pills. If using the liquid form, shake the bottle well before each dose.
Capsules (Vivlodex) are another once-daily option. An intravenous (IV) form (Anjeso, Xifyrm) is used only in hospitals for post-operative pain, administered as a 30 mg IV bolus once daily.
Your doctor will choose a starting dose based on your condition and health. For most adults, the typical starting dose is 7.5 mg once daily, with a 15 mg maximum daily dose. For children, the dose is based on body weight, not to exceed 7.5 mg per day.
Take meloxicam at the same time each day. It can be taken with or without food, but taking it with food or milk can help reduce stomach upset.
What to Do If You Miss a Dose or Overdose
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one and resume your regular schedule. Never double up on doses, as this increases side effect risks without adding benefit.
An overdose is a medical emergency. Symptoms can include extreme drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, severe stomach pain, and in severe cases, GI bleeding, kidney failure, breathing difficulty, or coma. Treatment is supportive as there is no specific antidote.
If you suspect an overdose, call the poison control helpline immediately at 1-800-222-1222 or get help online at https://www.poisonhelp.org/help. If the person has collapsed, is having a seizure, can’t be awakened, or is having trouble breathing, call 911 right away.
Safe Storage and Disposal
Properly storing and disposing of meloxicam protects your family, pets, and the environment.
For storage, keep meloxicam in its original container, tightly closed, at room temperature (68°F to 77°F), away from heat and moisture. Avoid the humid bathroom medicine cabinet. Keep all medications out of reach of children and pets; child-resistant caps are not foolproof. For more safety tips, visit http://www.upandaway.org.
For disposal, do not flush meloxicam or pour it down a drain. The best option is a medicine take-back program. Your pharmacist can help you find one, or you can find information on medicine take-back programs online.
If a take-back program is unavailable, dispose of it in your household trash. Mix the medication with an undesirable substance like used coffee grounds, seal it in a plastic bag, and throw it away. Black out personal information on the label. Ask your pharmacist for specific disposal instructions if you are unsure.
Frequently Asked Questions about Meloxicam
We hear a lot of questions from people trying to understand what is meloxicam and whether it’s the right choice for their pain management. Let’s tackle some of the most common concerns.
Is meloxicam a narcotic or a strong painkiller?
No, meloxicam is not a narcotic. It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and works differently from opioids. Opioids are addictive because they block pain signals and trigger the brain’s reward system. Meloxicam is not addictive; it works at the source of pain by blocking prostaglandins—the chemicals that cause inflammation—and does not affect the brain’s reward pathways.
Meloxicam is an effective pain reliever for inflammation-related pain like arthritis. While not addictive, some people with chronic pain may misuse it by taking more than prescribed. This is dangerous and increases the risk of serious side effects. Honest communication with your doctor about your pain is crucial.
What are the potential drug interactions with meloxicam?
Meloxicam interacts with many medications, which can reduce their effectiveness or increase risks. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and supplements.
- Other NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen): Do not combine with meloxicam. This greatly increases the risk of stomach bleeding and ulcers without added pain relief.
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin) and low-dose aspirin: Combining these with meloxicam increases bleeding risk. Close medical monitoring is essential.
- Blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors, ARBs) and Diuretics (water pills): Meloxicam can reduce their effectiveness and stress the kidneys, especially in older or dehydrated individuals. This can lead to fluid retention and higher blood pressure.
- Lithium and Methotrexate: Meloxicam can increase blood levels of these drugs to toxic levels, requiring regular monitoring by your doctor.
- Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs) and Corticosteroids (prednisone): These increase the risk of bleeding and stomach ulcers when taken with meloxicam.
- Other interactions include cyclosporine (kidney damage risk), digoxin (higher levels), and cholestyramine (faster meloxicam elimination).
The bottom line: Keep an updated medication list and share it with all your healthcare providers.
Are there precautions for specific groups like pregnant women or the elderly?
Yes. Certain groups face higher risks and need extra caution or should avoid meloxicam.
- Pregnant or planning pregnancy: The FDA warns against using NSAIDs like meloxicam at 20 weeks of pregnancy or later due to risks of kidney harm to the baby and low amniotic fluid. After 30 weeks, it can cause serious heart complications in the baby. NSAIDs may also temporarily delay ovulation. If breastfeeding, consult your doctor.
- Elderly patients (65+): This group faces higher risks of GI bleeding, heart attacks, and strokes from NSAIDs. Slower kidney and liver function can cause the drug to stay in the system longer. The Beers Criteria flags NSAIDs for careful use in older adults. Doctors usually prescribe lower doses and monitor patients closely.
- Kidney, liver, or heart disease: Use meloxicam with caution as it can worsen these conditions. Your doctor will weigh the benefits against the risks and may adjust your treatment.
- Asthma: Be cautious if you have had past reactions to aspirin or other NSAIDs, as severe reactions like breathing difficulty can occur.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important for everyone on meloxicam, especially those with kidney concerns, to reduce the risk of kidney problems.
The key takeaway is to be honest with your healthcare team about your full medical history to ensure meloxicam is a safe choice for you.
Conclusion: Using Meloxicam Safely and Responsibly
In summary, what is meloxicam? It’s a prescription NSAID that helps millions manage chronic pain from arthritis. As a non-narcotic, it can significantly improve quality of life by helping people stay active.
However, understanding meloxicam means recognizing its benefits and its serious risks, including heart attack, stroke, and gastrointestinal bleeding. These are real concerns that require your attention.
Safe use requires a partnership with your healthcare team. Take only the prescribed dose for the shortest time needed, never adjust it yourself, be honest about your medical history, and report any warning signs immediately.
Regular communication with your doctor is essential, as your response to the medication can change. Check-ins ensure meloxicam remains the right choice for you.
Living with chronic pain is exhausting. If you or a loved one are struggling with concerns about pain medication use or taking more than prescribed, help is available. There is no shame in reaching out.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
At Addiction Helpline America, we’re here to provide free, confidential support without judgment. Our team understands the complex relationship between chronic pain and medication concerns, and we’re committed to connecting you with resources and treatment options that address both pain management and recovery. Whether you’re in Alabama, California, Florida, New York, Texas, or anywhere else across the United States, we can help you find personalized solutions that work for your unique situation.
You deserve to live without overwhelming pain, and you deserve to do so safely. Let us help you find that balance.
Find personalized addiction treatment options
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.