Introduction
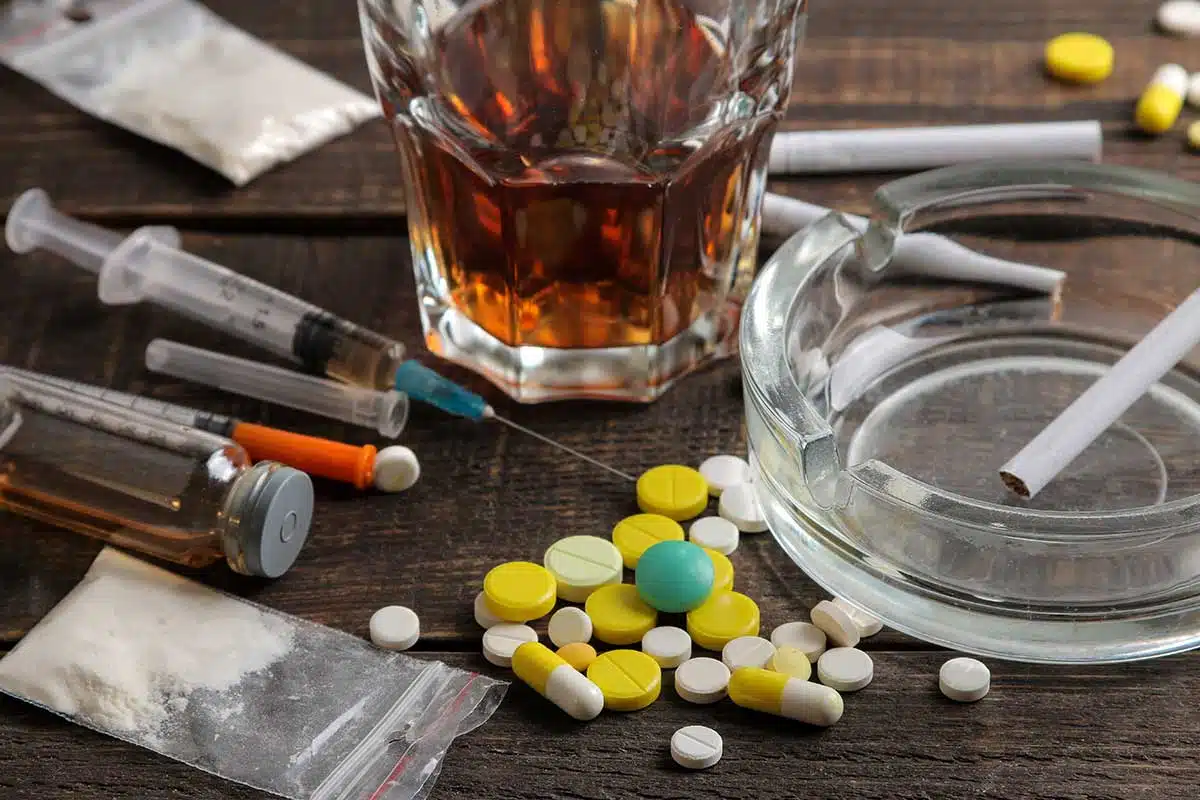
Drug addiction is a serious and widespread issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Some drugs are more addictive than others due to their chemical composition and how they impact the brain. Understanding which is the most addictive drug can help individuals make informed choices and seek help if needed.
Drugs with high addiction potential often produce intense pleasure or euphoria, quickly altering brain chemistry and reinforcing repeated use. Over time, this can lead to dependency, physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms, and significant health problems.
This article explores the most addictive drugs, their effects, and how individuals struggling with substance use disorder can seek treatment.
Factors That Make a Drug Addictive
Not all drugs have the same level of addictiveness. Several factors determine how addictive a drug can be:
1. Dopamine Release
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter responsible for pleasure and reward. Some substances flood the brain with dopamine, creating an intense feeling of euphoria. This “high” reinforces repeated use, increasing addiction potential.
2. Withdrawal Symptoms
The severity of withdrawal symptoms plays a significant role in addiction. Drugs that cause painful or distressing withdrawal symptoms, such as heroin or alcohol, make it harder for users to quit without professional help.
3. Tolerance Development
Tolerance occurs when a person needs increasing amounts of a substance to achieve the same effects. Rapid tolerance development often leads to higher consumption, increasing the risk of dependence and overdose.
4. Method of Administration
The way a drug is consumed affects its addictiveness. Smoking, injecting, or snorting substances can lead to a faster onset of effects, making them more addictive than those taken orally.
5. Availability and Social Acceptance
Legal and widely available substances, such as nicotine and alcohol, contribute to higher addiction rates. Social factors, peer pressure, and cultural acceptance also influence addiction potential.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
The Most Addictive Drugs Ranked
1. Heroin
Heroin is considered one of the most addictive drugs due to its powerful effects on the brain. It binds to opioid receptors, creating an intense feeling of euphoria and pain relief.
Addiction Potential
- Extremely high; many users develop addiction after just a few uses.
- Produces a strong and immediate high, increasing repeated use.
Withdrawal Symptoms
- Severe flu-like symptoms, including nausea, muscle pain, sweating, anxiety, and cravings.
- Psychological withdrawal can last for months, making relapse common.
Health Risks
- Increased risk of overdose, respiratory failure, and infectious diseases (HIV, hepatitis) from needle use.
- Long-term effects include brain damage, liver disease, and collapsed veins.
Statistics
- According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), nearly 1 million people in the U.S. reported using heroin in the past year.
- Overdose deaths involving heroin have increased significantly over the past decade.
2. Cocaine (Crack and Powdered Cocaine)
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant that increases dopamine levels in the brain, leading to intense feelings of energy, confidence, and euphoria.
Addiction Potential
- High; crack cocaine is even more addictive due to its fast-acting effects.
- Short-lived high leads to frequent use and binge patterns.
Withdrawal Symptoms
- Fatigue, depression, anxiety, agitation, and intense cravings.
- “Crash” phase can last for days, making relapse likely.
Health Risks
- Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and high blood pressure.
- Long-term effects include paranoia, psychosis, and cognitive impairment.
Statistics
- Around 1.5 million Americans reported cocaine use in a single year.
- Crack cocaine is more prevalent in lower-income communities, leading to severe addiction issues.
3. Methamphetamine (Meth)
Meth is another highly addictive stimulant that causes severe physical and mental health problems. It alters brain chemistry, leading to long-term damage.
Addiction Potential
- Very high; meth rapidly changes brain structure and function, making users dependent quickly.
- The euphoric high can last for hours, leading to prolonged use and addiction.
Withdrawal Symptoms
- Anxiety, paranoia, extreme fatigue, hallucinations, and depression.
- Meth withdrawal is often accompanied by severe cravings and violent mood swings.
Health Risks
- Extreme weight loss, dental problems (“meth mouth”), and skin sores.
- Long-term use can cause brain damage, memory loss, and increased risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Statistics
- Over 2.5 million Americans have reported meth use in the past year.
- Meth-related overdose deaths have risen dramatically in recent years.
4. Nicotine
Nicotine is found in tobacco products and is one of the most widely used addictive substances in the world.
Addiction Potential
- High; nicotine addiction can develop quickly, even after a few cigarettes.
- Smoking triggers dopamine release, reinforcing compulsive use.
Withdrawal Symptoms
- Irritability, intense cravings, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, and weight gain.
- Many smokers struggle with multiple quit attempts before achieving success.
Health Risks
- Increased risk of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and chronic respiratory illnesses.
- Secondhand smoke exposure can harm non-smokers.
Statistics
- Approximately 28 million adults in the U.S. smoke cigarettes.
- Smoking-related illnesses cause nearly half a million deaths annually.
5. Alcohol
Alcohol is a legal but highly addictive substance that affects both physical and mental health.
Addiction Potential
- Moderate to high; dependency can develop over time with repeated use.
- Many people underestimate alcohol’s addictive potential due to social acceptance.
Withdrawal Symptoms
- Anxiety, tremors, seizures, and hallucinations in severe cases.
- Delirium tremens (DTs) can be life-threatening.
Health Risks
- Liver disease, heart problems, brain damage, and increased cancer risk.
- Alcohol-related accidents contribute to thousands of deaths annually.
Statistics
- Nearly 15 million adults in the U.S. struggle with alcohol use disorder.
- Alcohol-related deaths exceed 140,000 per year in the U.S.
Other Highly Addictive Substances
Several other substances also have high addiction potential:
1. Prescription Opioids (Oxycodone, Fentanyl)
- Used for pain relief but highly addictive.
- Contributed to the opioid epidemic, with thousands of overdose deaths annually.
2. Benzodiazepines (Xanax, Valium)
- Prescribed for anxiety but can cause severe dependence.
- Withdrawal can be dangerous, leading to seizures and panic attacks.
3. Stimulants (Adderall, Ritalin)
- Often prescribed for ADHD but commonly abused.
- Long-term abuse can cause heart problems and mental health issues.
The Impact of Addiction on Mental Health
1. Psychological Effects of Addiction
Addiction has several psychological consequences:
- Alters brain chemistry, impacting mood, behavior, and thoughts.
- Common mental health issues caused by addiction include anxiety, depression, and paranoia.
- Can worsen pre-existing mental health conditions, making recovery harder.
2. Co-occurring Disorders and Addiction
Many individuals experience both addiction and mental health disorders simultaneously:
- Known as dual diagnosis.
- Treating both addiction and mental health disorders is crucial for effective recovery.
- Specialized programs that address both issues simultaneously provide better outcomes.
3. How Addiction Can Affect Brain Function
Addiction changes the brain’s reward system:
- Dopamine release is increased, reinforcing substance use.
- Over time, the brain becomes reliant on substances to feel “normal.”
- Leads to cognitive impairments, emotional numbness, and poor decision-making.
The Stages of Addiction
1. Experimentation and Casual Use
The initial stage of addiction often involves:
- Curiosity or peer pressure leading to initial use.
- No immediate negative consequences, but regular use may follow.
2. Regular Use and Tolerance
As substance use increases:
- Tolerance develops, meaning larger amounts are needed to feel the same effects.
- This phase marks the beginning of habitual use.
3. Dependency and Addiction
At this point:
- Individuals become dependent on the substance, often experiencing withdrawal symptoms when they stop.
- Substance use takes priority over responsibilities and relationships.
4. Recovery and Long-Term Sobriety
This phase involves:
- Actively seeking treatment and working on maintaining sobriety.
- It is often the most challenging phase, but with proper support, long-term recovery is achievable.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
The Role of Family and Friends in Addiction Recovery
1. How Loved Ones Can Support the Recovery Process
Family and friends can provide critical support:
- Encourage the individual in their recovery journey.
- Offer emotional support and motivation.
- Understand that recovery takes time and patience.
2. The Importance of Family Therapy
Family therapy helps:
- Improve communication within the family.
- Address conflicts and unhealthy dynamics.
- Strengthen the support system for the individual in recovery.
3. Setting Healthy Boundaries During Recovery
It is vital to:
- Establish clear boundaries to prevent enabling behaviors.
- Protect both the individual’s and the family’s emotional health.
- Encourage accountability and responsibility during recovery.
The Dangers of Mixing Drugs and Alcohol
1. Increased Risk of Overdose
Mixing drugs and alcohol increases:
- The risk of overdose due to compounded effects on the body.
- Respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and death can result from mixing substances.
2. How Mixing Affects the Body
Combining substances can:
- Lead to unpredictable and dangerous effects.
- Alcohol, as a depressant, can amplify the effects of other substances, increasing health risks.
3. The Role of Stimulants and Depressants in Addiction
When mixed, stimulants and depressants:
- Can lead to conflicting effects on the body.
- Create a “dangerous cocktail” that strains the heart, liver, and brain.
- Increase the likelihood of addiction and overdose.
Treatment for Specific Substances
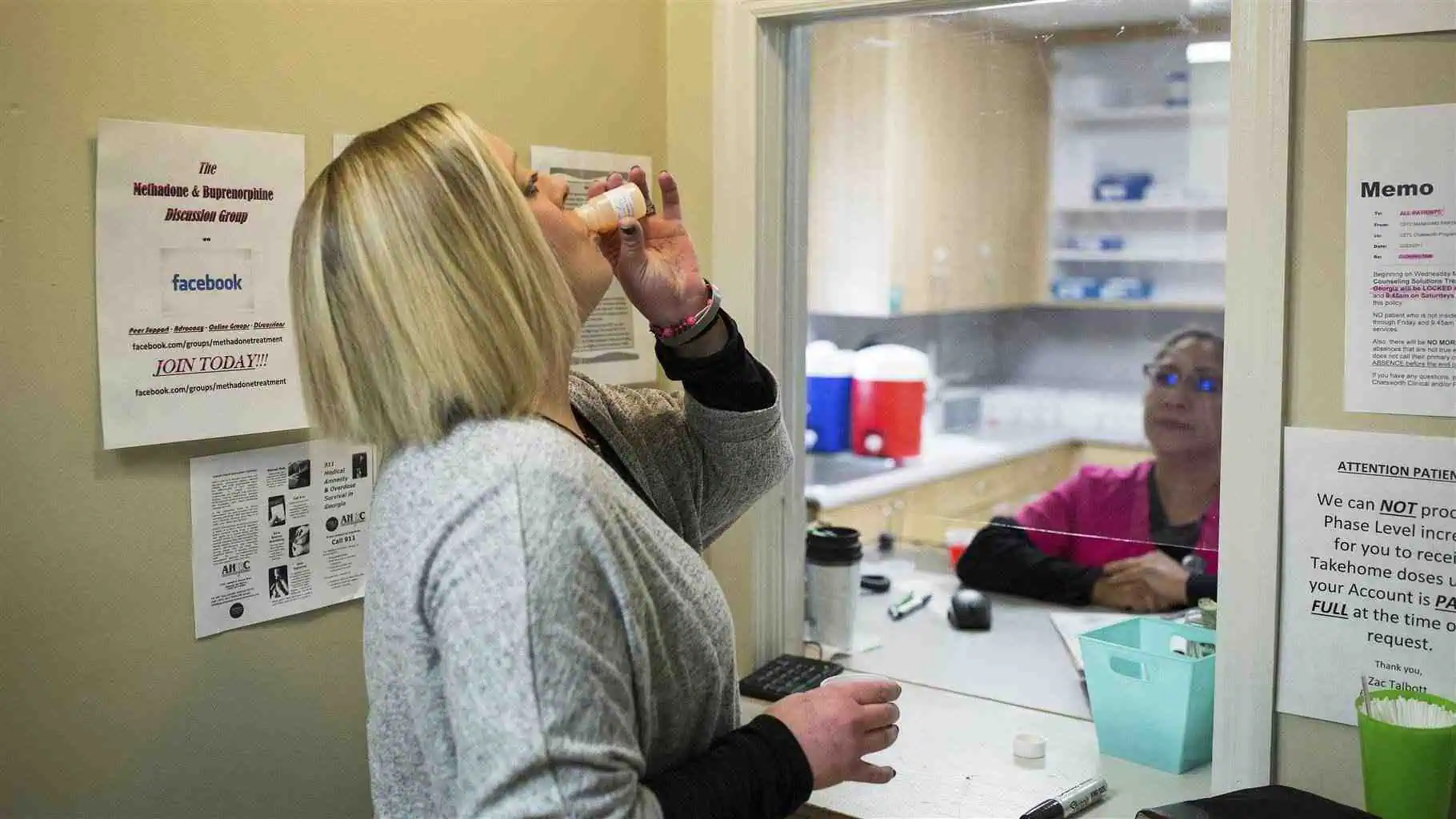
1. Treatment for Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction treatment may include:
- Detoxification to manage withdrawal.
- Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) with methadone or buprenorphine.
- Counseling and therapy to address the psychological aspects of addiction.
2. Treatment for Alcohol Addiction
Alcohol addiction treatment generally involves:
- Medically supervised detox.
- Therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Inpatient or outpatient rehab programs to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
3. Treatment for Stimulant Addiction (Cocaine, Meth)
Treatment for stimulant addiction often focuses on:
- Behavioral therapy such as contingency management and CBT.
- Research into medications to treat stimulant addiction is ongoing, but therapy is key.
4. Treatment for Nicotine Addiction
Nicotine addiction treatment options include:
- Behavioral therapy and counseling.
- Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) with patches, gums, and lozenges.
- Medications like varenicline and bupropion to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
How to Prevent Relapse
1. Identifying Triggers and High-Risk Situations
Relapse often occurs due to triggers, including:
- Stress, emotional pain, or environmental cues.
- Identifying and understanding these triggers is crucial in preventing relapse.
2. Building a Support System for Long-Term Recovery
Having a support network is key to:
- Building accountability through support groups like AA or NA.
- Encouraging positive relationships with family and friends.
3. Coping Strategies for Maintaining Sobriety
Healthy coping strategies include:
- Exercise, mindfulness, and meditation.
- Creative outlets like art or music to manage emotions without substances.
The Importance of Aftercare in Addiction Recovery
1. The Role of Ongoing Therapy and Counseling
Aftercare includes:
- Continued therapy to maintain progress and address new challenges.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches help individuals stay on track.
2. Support Groups: AA, NA, and Others
Support groups provide:
- Community support and shared experiences.
- Accountability and encouragement to stay sober long-term.
3. Continuing Medical Support and Checkups
Aftercare also involves:
- Regular checkups to ensure physical health and recovery.
- Monitoring for any underlying health issues or potential relapse signs.
How to Get Help for Addiction
If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, seeking help is crucial.
Signs of Addiction
- Increased tolerance, needing more of a substance for the same effect.
- Inability to stop or control use despite negative consequences.
- Withdrawal symptoms when not using.
- Neglecting responsibilities, relationships, and health due to substance use.
Treatment Options
- Detox Programs: Medical supervision to manage withdrawal safely.
- Inpatient Rehab: Structured treatment in a residential setting.
- Outpatient Rehab: Flexible treatment options while living at home.
- Therapy and Counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and support groups help with recovery.
Importance of Professional Rehab
Professional treatment offers the best chance for long-term recovery. Rehab centers provide medical support, therapy, and coping strategies to prevent relapse.
Conclusion
Addiction is a complex disease that affects millions of individuals worldwide. While some substances have a higher addiction potential than others, any drug misuse can lead to serious health consequences and dependency. Understanding which drugs are most addictive can help people recognize the risks and make informed choices about substance use.
If you or someone you love is struggling with addiction, it’s important to remember that help is available. Recovery is possible with the right treatment, support, and commitment. Taking the first step toward sobriety can be life-changing, leading to improved health, relationships, and overall well-being.
For immediate assistance, call Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Contact Addiction Helpline America
Addiction is a treatable condition, and help is available. If you or a loved one is battling substance abuse, contact Addiction Helpline America for guidance and support.
Call now: (844) 561-0606
Recovery is possible—taking the first step can change your life.
What makes a drug addictive?
What are the symptoms of addiction?
How can I get help for addiction?
What is the difference between inpatient and outpatient rehab?
Can addiction be cured?
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.