Understanding Gabapentin Withdrawal: What You Need to Know
Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can be challenging and dangerous. If you plan to stop taking this medication, here’s what you need to know:
Common Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms:
- Physical symptoms: Nausea, sweating, headaches, dizziness, tremors, increased heart rate, high blood pressure
- Psychological symptoms: Anxiety, panic attacks, insomnia, depression, confusion, restlessness
- Timeline: Symptoms typically begin within 12-48 hours after your last dose.
- Peak severity: Days 2-3 are usually the most intense.
- Duration: Acute symptoms often improve over 1-2 weeks, but some may last longer.
- Critical warning: Never stop gabapentin abruptly—this can trigger seizures, even if you don’t have epilepsy.
Most Important: Gabapentin should always be tapered gradually under medical supervision. The withdrawal process can mimic alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal and may require professional support. If you need immediate help, call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 for 24/7 guidance.
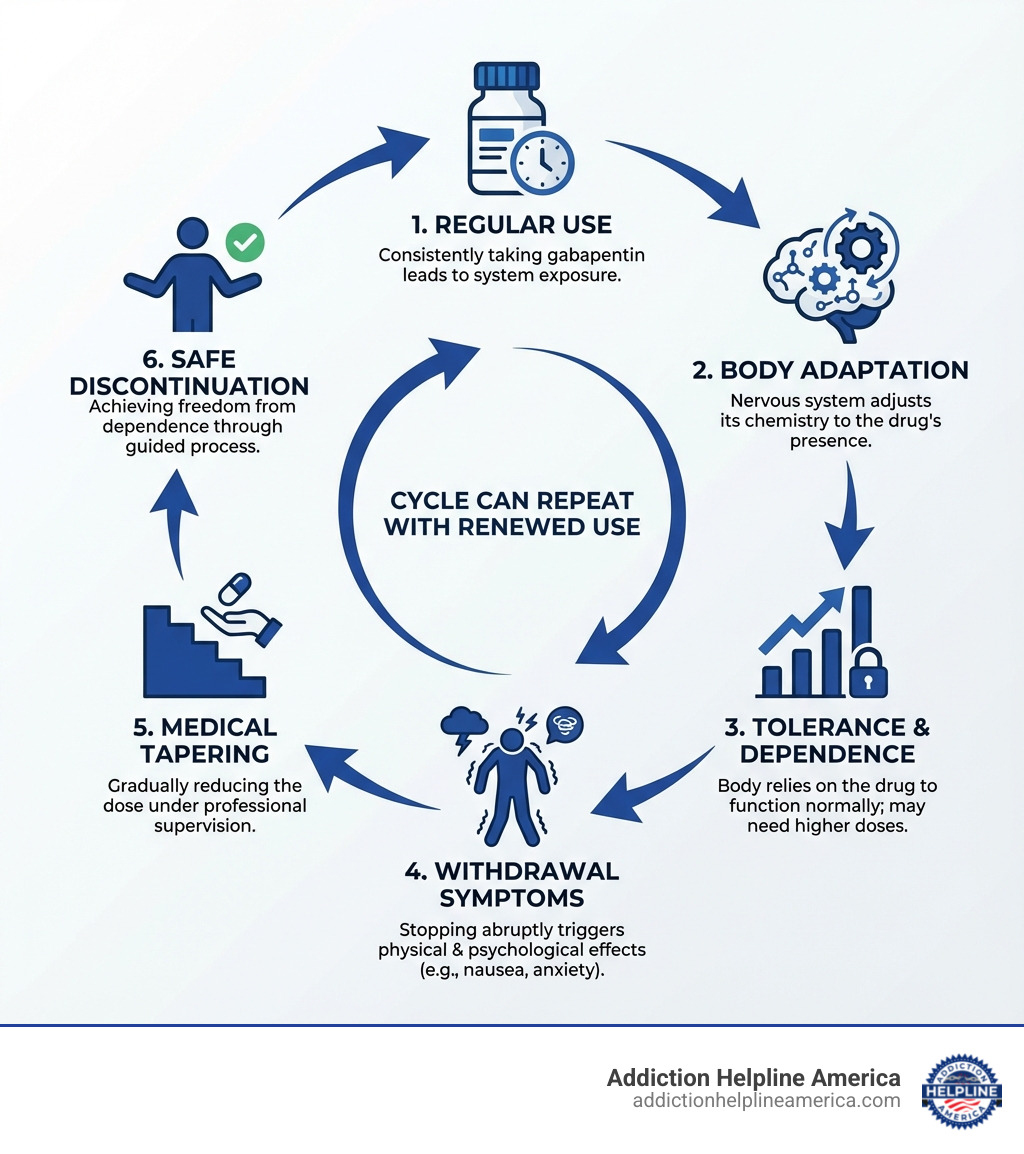
Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is an anticonvulsant that calms overactive nerve signals. When you take it regularly, your body adapts to its presence, a process called physical dependence. This means your body relies on the medication to function normally. When you stop, your body needs time to readjust, causing withdrawal symptoms.
The risk of withdrawal increases with higher doses, longer use (3+ weeks), and abrupt discontinuation. If you’re struggling with gabapentin dependence, help is available through Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606. Our experienced team provides 24/7 guidance to connect you with the right resources.
What is Gabapentin Prescribed For?
Gabapentin is an FDA-approved medication for:
- Epilepsy: As an adjunctive therapy for partial onset seizures.
- Postherpetic Neuralgia: Nerve pain that lingers after a shingles outbreak.
It is also frequently prescribed “off-label” for other conditions, including:
- Anxiety and sleep disorders
- Bipolar disorder
- Restless Legs Syndrome (Horizant formulation)
- Fibromyalgia and other neuropathic pain
In 2019, an estimated 69 million prescriptions were written in the U.S., making it one of the most prescribed drugs.
Why Does Withdrawal Occur?
Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms happen because of neuroadaptation. Your brain adjusts to the drug’s presence to maintain balance (homeostasis). It becomes physically dependent on gabapentin to function normally. When you suddenly stop, this balance is disrupted, triggering withdrawal symptoms.
It’s important to distinguish between physical dependence and addiction:
- Physical dependence is a physiological adaptation where the body expects the drug. Withdrawal occurs when it’s removed. This can happen even when taking gabapentin as prescribed.
- Addiction is a brain disease characterized by compulsive drug use despite negative consequences.
You can be physically dependent without being addicted. However, misusing gabapentin—taking high doses or mixing it with substances like opioids or alcohol—increases the risk of both dependence and addiction, leading to more severe withdrawal.
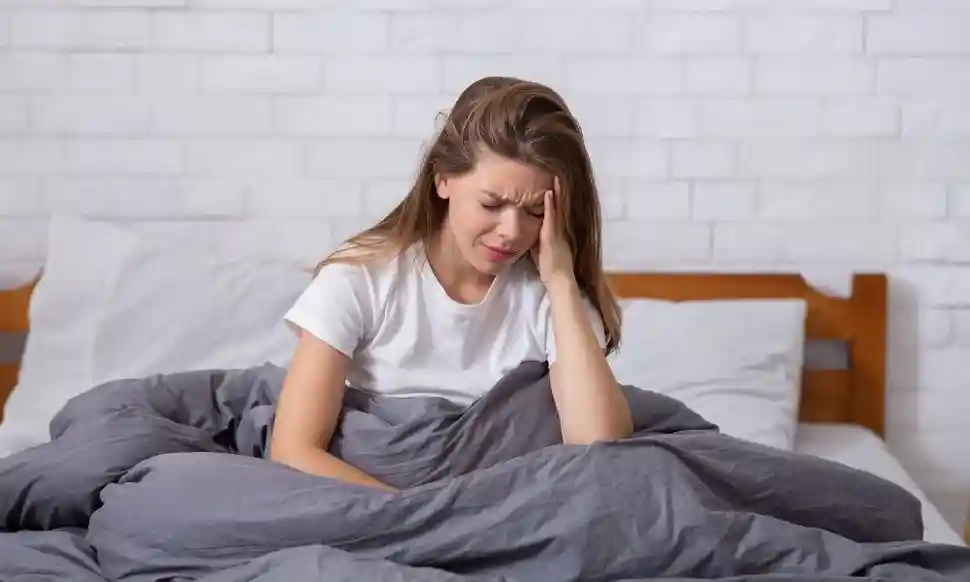
Recognizing the Common Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms
Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms typically begin within 12 to 48 hours after the last dose, with peak intensity around days 2 to 3. The experience is often compared to withdrawal from alcohol and benzodiazepines because gabapentin also calms nerve activity. Symptoms can be severe and may mimic other medical issues like the flu or a cardiac event, which is why medical supervision is critical. Don’t face this alone—call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 for immediate support.
Physical Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms
When your body reacts to the absence of gabapentin, it can manifest in various physical ways as it tries to regain balance. Common physical gabapentin withdrawal symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting: Feeling sick to your stomach.
- Sweating and chills: Excessive sweating (diaphoresis) or feeling cold.
- Headaches: Tension or migraine-like head pain.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or unsteady.
- Muscle and body aches: Generalized pain, stiffness, or cramping.
- Tremors or shaking: Involuntary trembling, especially in the hands.
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia): A pounding or racing heart.
- High blood pressure (hypertension): A rise in blood pressure.
- Gastrointestinal distress: Diarrhea or stomach cramps.
- Fatigue: A deep sense of tiredness and low energy.
- Restlessness (Akathisia): An inner unease and inability to sit still.
Psychological Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal can also profoundly affect your mental and emotional state. The brain becomes accustomed to gabapentin’s effects, and its absence can trigger a range of psychological challenges. Common psychological gabapentin withdrawal symptoms include:
- Anxiety and panic attacks: Intense worry, nervousness, or sudden episodes of dread.
- Irritability and agitation: Feeling easily annoyed, on edge, or restless.
- Depression and mood swings: Low mood, hopelessness, or rapid emotional shifts.
- Insomnia and sleep disturbances: Difficulty falling or staying asleep and vivid dreams.
- Confusion or disorientation: Trouble thinking clearly or remembering things.
- Restlessness (Akathisia): An inner compulsion to move, making it hard to relax.
- Psychotic symptoms: In rare, severe cases, hallucinations or delusions.
- Suicidal thoughts or behavior: A serious risk that requires immediate medical attention.
These psychological symptoms can be distressing and may cause “rebound symptoms,” where the original condition (like anxiety) returns or worsens. If you or a loved one are struggling, especially with suicidal thoughts, please reach out for help immediately. Call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 to connect with support right away.
The Gabapentin Withdrawal Timeline and Duration
Understanding the timeline for gabapentin withdrawal symptoms helps you know what to expect. The duration and severity of withdrawal depend on several factors:
- Dosage: Higher doses often lead to more intense withdrawal.
- Duration of Use: Long-term use (3+ weeks) can result in a more challenging withdrawal.
- Individual Health: Your metabolism, physical, and mental health play a role.
- Abruptness of Discontinuation: Stopping “cold turkey” causes more severe symptoms than a gradual taper.
- Polysubstance Use: Using other substances can complicate withdrawal.
The process moves from acute symptoms to a potential post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS).
Early Withdrawal (First 1-2 Days)
The initial gabapentin withdrawal symptoms begin quickly, often within 12 to 48 hours of the last dose. This is your body’s first reaction to the medication’s absence. Early symptoms include:
- Anxiety and nervousness
- Insomnia
- Sweating
- Restlessness and agitation
Peak Withdrawal (Days 2-7)
This is the most intense phase, with gabapentin withdrawal symptoms reaching their peak between days 2 and 3. Both physical and psychological symptoms are at their most severe. During this critical time, you might experience:
- Severe anxiety and panic attacks
- Pronounced physical symptoms like nausea, headaches, and tremors
- Significant sleep disturbances
- Mood swings, irritability, and confusion
- Increased risk of rebound seizures, especially for those with epilepsy
This period can feel overwhelming and is dangerous to manage alone. For immediate guidance, call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 for support and connection to appropriate care.
Late Withdrawal (1-2 Weeks and Beyond)
After the peak, acute gabapentin withdrawal symptoms gradually improve over the next 1 to 2 weeks. However, some issues may linger, such as anxiety, insomnia, or low mood.
For some, particularly after long-term or high-dose use, Post-Acute Withdrawal Syndrome (PAWS) can occur. PAWS involves less intense but persistent symptoms like mood swings, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating that can last for weeks or months.
Ongoing support is crucial for managing these long-term symptoms. Support groups provide community and encouragement. For more information on long-term recovery, explore our guide on Support Groups for Addiction or call us at 844-561-0606 to discuss your options.
Safe Discontinuation and Managing Withdrawal
Discontinuing gabapentin requires caution. Abruptly stopping, or going “cold turkey,” can trigger a cascade of severe and potentially life-threatening gabapentin withdrawal symptoms.
The most critical risk is rebound seizures, which can occur even in people without a history of epilepsy. For those with epilepsy, sudden cessation can lead to status epilepticus—a medical emergency involving prolonged seizures. Abruptly stopping also triggers intense psychological distress, including severe anxiety and panic attacks.
Professional medical guidance is essential for safety. Trying to manage withdrawal alone is not only difficult but also dangerous. Call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 to get connected with professional help immediately. Understanding The Role of Detox in Rehab is a crucial first step.
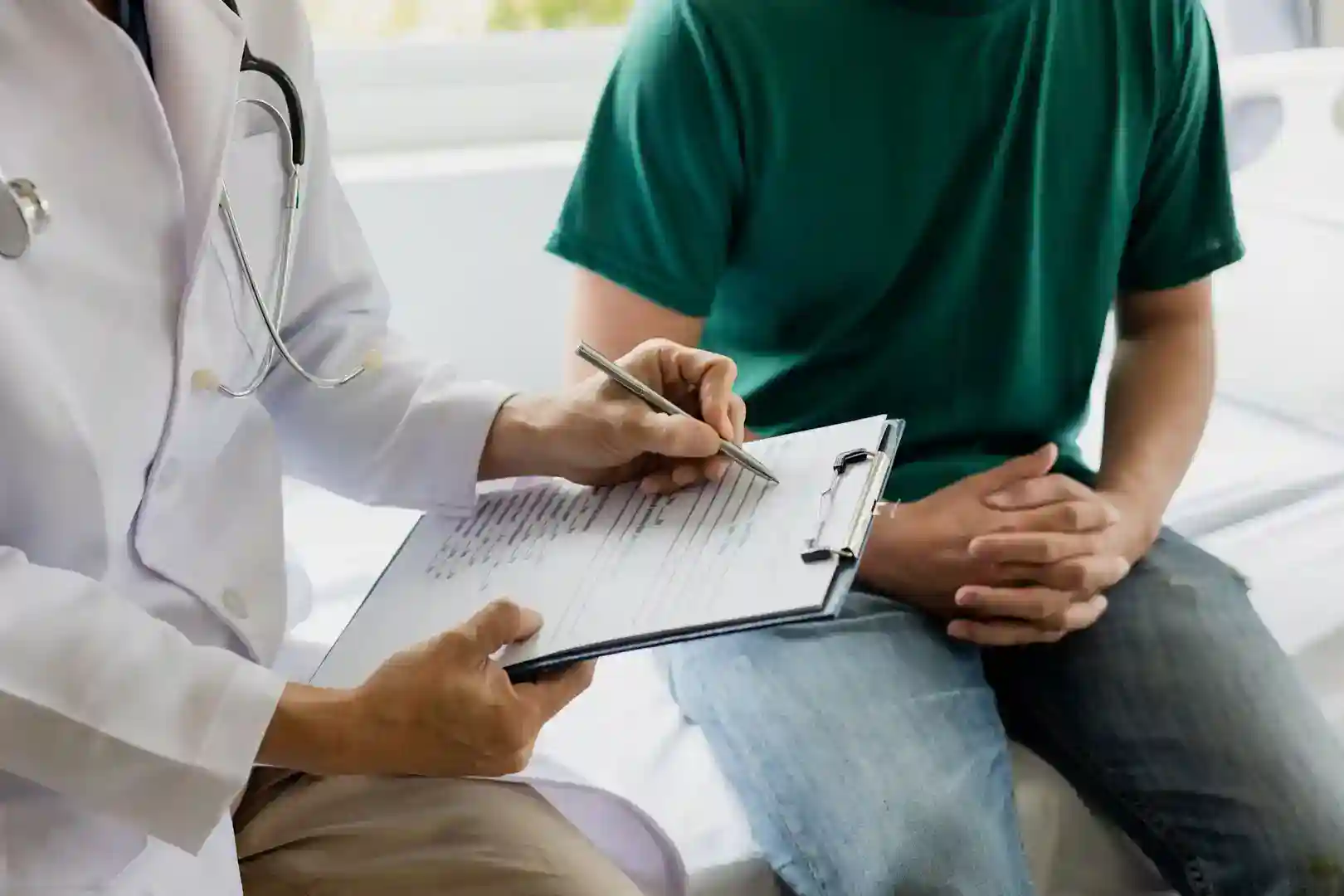
The Importance of a Medically-Supervised Taper
A medically supervised taper is the safest way to discontinue gabapentin. This gradual dose reduction allows your brain and body to readjust slowly, minimizing the intensity of withdrawal symptoms. A taper plan should be similar to a benzodiazepine taper—slow and steady over weeks or months.
A healthcare provider will:
- Assess your individual needs (dosage, duration of use, health).
- Develop a personalized tapering schedule (e.g., reducing the dose by 300mg every 4 days, or slower for some individuals).
- Monitor your symptoms and adjust the taper as needed.
- Provide support and strategies for managing discomfort.
This methodical approach significantly reduces risks. If you need help finding a provider to guide you, call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 to connect with appropriate resources.
Treatment Options and Professional Support
Professional support is key to navigating gabapentin withdrawal symptoms safely. Addiction Helpline America connects you with the best treatment options nationwide. Call us at 844-561-0606 to discuss your specific needs.
- Medical Detox Programs: This is often the first step. In a detox facility, professionals provide 24/7 supervision to manage withdrawal safely, prevent complications like seizures, and administer medications to ease discomfort.
- Inpatient vs. Outpatient Rehab: Inpatient rehab offers 24/7 care in a structured, trigger-free environment, ideal for severe dependence or co-occurring conditions. Outpatient programs (PHPs, IOPs) provide structured therapy with more flexibility, allowing you to live at home.
- Behavioral Therapies (CBT): Cognitive Behavioral Therapy helps you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to drug use, equipping you with coping skills.
- Managing Co-occurring Disorders: Effective treatment addresses both substance dependence and underlying mental health conditions like anxiety or depression simultaneously (dual diagnosis treatment). Our Dual Diagnosis Treatment Costa Mesa Guide offers more insight.
To find facilities near you, explore our resources on Drug Detox and Rehab Facilities Near Me or call 844-561-0606 for personalized assistance.
Self-Management and Coping Strategies
While professional guidance is essential, these self-care strategies can support your recovery:
- Hydration and Nutrition: Drink plenty of water and eat a balanced diet. Avoid excessive sugar and caffeine.
- Calming Techniques: Practice mindfulness, deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga to reduce anxiety.
- Gentle Exercise: Light activity like walking can boost mood and improve sleep. Listen to your body.
- Journaling: Track your symptoms and progress to share with your provider and stay motivated.
- Sleep Routine: Establish a consistent, relaxing bedtime routine to improve sleep quality.
Always discuss these strategies with your healthcare provider to ensure they are right for you.
Frequently Asked Questions about Gabapentin Withdrawal
Here are answers to common concerns about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms. If you have additional questions, don’t hesitate to call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606.
Are there specific risks for older adults during withdrawal?
Yes, older adults face unique risks during gabapentin withdrawal. Due to age-related physiological changes like slower metabolism, they may be more sensitive to dose changes. Case reports show that withdrawal in geriatric patients can be severe, with symptoms like profound confusion, chest pain, and hypertension, even after a gradual taper. These symptoms can be mistaken for other health problems.
For these reasons, a gabapentin taper for older adults should be exceptionally slow, often extending over weeks to months, similar to a benzodiazepine taper. For more details, you can consult this review of withdrawal in an older adult. If you’re caring for an older adult going through withdrawal, call us at 844-561-0606 for specialized guidance.
Can gabapentin withdrawal be life-threatening?
While manageable with medical supervision, gabapentin withdrawal can have life-threatening risks, particularly if stopped abruptly. The primary danger is status epilepticus, a condition of prolonged or repeated seizures. Even people without a history of epilepsy can experience seizures.
Other severe risks include:
- Severe Hypertension: Uncontrolled high blood pressure.
- Psychotic Symptoms: Rare instances of hallucinations or delusions.
- Suicidal Thoughts or Behavior: A serious risk requiring immediate medical attention.
These outcomes are largely preventable with a medically supervised, gradual taper. Never stop gabapentin “cold turkey.” If you or someone you know experiences severe symptoms or suicidal thoughts, seek immediate medical help. You can find a Crisis Support Line or call 911. For non-emergency support and guidance, call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606.
How is physical dependence different from addiction?
Understanding the difference is key when discussing gabapentin withdrawal symptoms.
- Physical Dependence: A physiological state where the body adapts to a drug. Withdrawal symptoms occur when the drug is stopped. This can happen even when taking gabapentin exactly as prescribed.
- Addiction: A chronic brain disease involving compulsive drug-seeking and use despite harmful consequences.
In short, you can be physically dependent on gabapentin without being addicted. However, misusing the drug increases the risk of developing both. If you suspect addiction is a factor, call Addiction Helpline America at 844-561-0606 or Explore Treatment Options to better understand your situation and find the right help.
Conclusion: Taking the First Step to a Safe Recovery
Navigating gabapentin withdrawal symptoms is a serious challenge, but recovery is entirely possible with the right support. The most important takeaway is that you should never stop taking gabapentin abruptly. A medically supervised taper is essential for your safety and comfort.
Recovery from gabapentin dependence begins with a comprehensive treatment plan. At Addiction Helpline America, we are committed to providing free, confidential, and personalized guidance to help you find the right program from our extensive network of treatment centers across the U.S. Call us today at 844-561-0606 to speak with a compassionate specialist who understands what you’re going through.
Do not let the fear of withdrawal keep you from a healthier future. Your journey to recovery starts with one courageous step. For a personalized assessment and to find the support you need, call 844-561-0606 or visit Addiction Helpline America online and learn more with our addiction complete guide. We are here to help you every step of the way—you don’t have to face this alone. Call 844-561-0606 now and take the first step toward freedom from gabapentin dependence.
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.