Introduction
Drug addiction is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including environmental, psychological, and biological elements. One of the most debated questions in addiction research is whether drug addiction is genetic. Scientists have explored the role of genetics in addiction, identifying how hereditary factors might contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to substance abuse. While genetics play a role, environmental influences also significantly impact addiction development.
This article delves into the genetic factors linked to addiction, how family history affects risk, and the interaction between genes and the environment in substance use disorders.
Understanding Drug Addiction
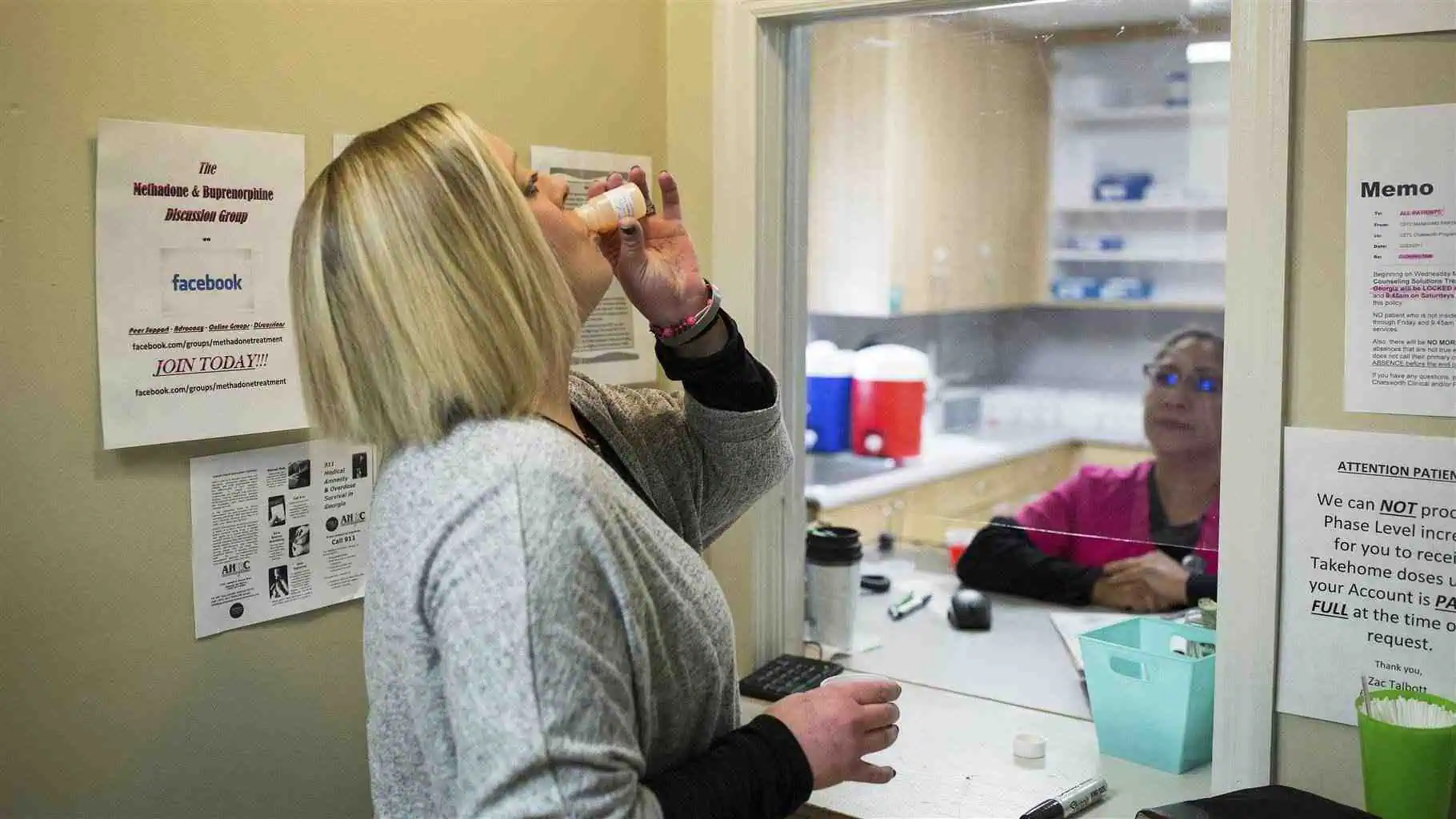
Drug addiction, also known as substance use disorder (SUD), is a chronic disease that affects brain function and behavior. It leads to compulsive drug-seeking despite harmful consequences. Addiction impacts the brain’s reward system, altering dopamine levels and reinforcing drug use.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Commonly Abused Substances
- Opioids (Heroin, Prescription Painkillers) – Highly addictive substances that alter pain perception and induce euphoria.
- Cocaine – A stimulant that increases energy and confidence while causing severe withdrawal symptoms.
- Methamphetamine – A powerful stimulant known for its high addiction potential.
- Alcohol – One of the most commonly abused substances, with both genetic and environmental influences.
- Marijuana – While considered less addictive, prolonged use can lead to dependency.
Causes of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction results from a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. These include:
- Genetics – Family history of addiction increases risk.
- Mental Health Disorders – Anxiety, depression, and PTSD contribute to substance abuse.
- Environmental Exposure – Peer pressure, trauma, and early exposure to drugs play a role.
- Brain Chemistry – Some individuals may be more prone to addiction due to dopamine regulation differences.
Is Drug Addiction Genetic?
The Role of Genetics in Addiction
Genetics account for 40–60% of a person’s vulnerability to addiction, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Scientists have identified several genes that influence addiction risk, including those affecting dopamine receptors and metabolism.
Genes Linked to Addiction
- Dopamine Receptor Genes (DRD2) – Plays a crucial role in the brain’s reward system. People with a specific DRD2 gene variant may have a higher addiction risk.
- COMT Gene – Regulates dopamine levels; variations can affect impulse control and drug dependence.
- OPRM1 Gene – Influences opioid addiction risk by affecting how the body responds to painkillers and heroin.
- CHRNA5 Gene – Linked to nicotine addiction; affects how the brain reacts to tobacco.
- ADH1B and ALDH2 Genes – Impact alcohol metabolism and addiction vulnerability.
Family History and Addiction
A person with an addicted parent or sibling is at a significantly higher risk of developing a substance use disorder. Studies show that children of addicts are 8 times more likely to develop addiction themselves. However, having a genetic predisposition does not mean addiction is inevitable.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Nature vs. Nurture: The Genetic-Environmental Interaction
How Environment Shapes Addiction Risk
While genetics play a role, environmental factors significantly influence addiction development. These include:
- Parental Influence – Children raised in households with addiction exposure may normalize substance use.
- Peer Pressure – Social circles can encourage drug experimentation.
- Childhood Trauma – Abuse, neglect, and stress can trigger substance abuse as a coping mechanism.
- Socioeconomic Status – Poverty and lack of education increase drug use risk.
Epigenetics: How Environment Alters Gene Expression
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression caused by environmental influences. Stress, trauma, and drug exposure can “turn on” or “turn off” certain genes, increasing addiction risk. For example, chronic stress can activate addiction-related genes, making individuals more susceptible to substance abuse.
Scientific Studies on Genetic Links to Addiction
Twin and Adoption Studies
Researchers study twins and adopted individuals to determine genetic influences on addiction.
- Twin Studies: Identical twins share 100% of their genes, while fraternal twins share about 50%. Studies show that if one identical twin has an addiction, the other has a 50–70% chance of also developing it.
- Adoption Studies: Children of biological parents with addiction but raised in non-addicted households still show a higher risk of addiction, proving a genetic link.
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
GWAS research has identified hundreds of genetic variations associated with addiction. Scientists continue to explore how these genetic markers interact with environmental triggers.
Can Addiction Be Prevented If It’s Genetic?
Even if a person has a genetic predisposition, addiction is not unavoidable. Several strategies can help prevent substance abuse:
Early Intervention and Awareness
- Genetic Counseling – Individuals with a family history of addiction can seek professional guidance.
- Education Programs – Teaching adolescents about addiction risks can prevent early drug use.
Healthy Coping Mechanisms
- Stress Management – Yoga, meditation, and exercise help reduce the urge to use drugs.
- Therapy – Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps individuals cope with triggers.
Strong Support Systems
- Family Involvement – Open discussions about addiction risks can deter drug use.
- Community Resources – Support groups, rehab centers, and counseling can provide assistance.
Treatment Options for Addiction
If addiction develops, various treatment options are available:
Medical Detoxification
The first step in addiction recovery is detox, where the body clears the substance. Detox should be done under medical supervision to manage withdrawal symptoms.
Behavioral Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps individuals identify and change destructive thought patterns.
- Motivational Interviewing (MI) – Encourages self-motivation for recovery.
- Contingency Management (CM) – Uses rewards to reinforce positive behavior.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Certain medications help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms:
- Methadone and Buprenorphine – For opioid addiction.
- Naltrexone – Blocks the effects of opioids and alcohol.
- Bupropion and Varenicline – Help with nicotine addiction.
Support Groups and Rehabilitation
- 12-Step Programs (AA, NA) – Provide peer support and guidance.
- Inpatient and Outpatient Rehab – Structured programs for recovery.
- Counseling Services – Help address underlying causes of addiction.
Statistics on Addiction and Genetics
National Addiction Statistics
- 50% of addiction risk is genetic, according to research from the American Psychological Association (APA).
- 21 million Americans suffer from substance use disorder.
- Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) affects 14.5 million adults in the U.S.
State and City-Specific Data
To provide localized information, addictionhelplineamerica.com includes state and city-specific addiction statistics. Check our resources for more detailed statistics on addiction in your area.
The Role of Neurotransmitters in Addiction and Genetics
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the brain that play a crucial role in regulating mood, emotions, and behavior. Many addictive substances alter neurotransmitter function, reinforcing drug-seeking behaviors. Genetics influence how these neurotransmitters function, which can make some individuals more prone to addiction than others.
Key Neurotransmitters Involved in Addiction
- Dopamine – Known as the “reward chemical,” dopamine is central to addiction. It creates pleasurable feelings when a person engages in rewarding activities, such as eating or socializing. Drugs artificially increase dopamine levels, reinforcing drug use. Genetic variations in dopamine receptor genes, such as DRD2, can make some individuals more susceptible to addiction.
- Serotonin – This neurotransmitter regulates mood and emotional stability. People with genetic mutations affecting serotonin transporters (such as 5-HTTLPR) may be more prone to anxiety and depression, increasing their likelihood of using drugs as a coping mechanism.
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) – GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps calm brain activity. Substances like alcohol enhance GABA’s effects, leading to relaxation. Genetic variations affecting GABA receptors can influence a person’s risk of developing alcohol dependence.
- Glutamate – This neurotransmitter is involved in learning and memory. Drugs can cause long-term changes in glutamate signaling, which may contribute to cravings and relapse.
How Genetic Variations Affect Addiction Risk
Some individuals have genetic mutations that make their neurotransmitter systems more sensitive to drugs. For example:
- People with a low-functioning DRD2 receptor gene may require more dopamine stimulation to feel pleasure, making them more prone to addiction.
- Genetic mutations in serotonin transporters can increase impulsivity, leading to higher substance abuse risk.
Understanding how neurotransmitters and genetics interact can help in developing personalized addiction treatments, such as medications targeting specific neurotransmitter imbalances.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Ethnic and Gender Differences in Genetic Addiction Risk
Genetic factors influencing addiction can vary based on ethnicity and gender, leading to different levels of susceptibility across populations.
Genetic Differences Across Ethnic Groups
Studies suggest that certain genetic variations related to addiction are more prevalent in specific ethnic groups.
- Alcohol Metabolism Genes (ADH1B and ALDH2) –
- These genes affect how quickly alcohol is broken down in the body.
- People of East Asian descent often carry a genetic mutation that leads to flushing, nausea, and rapid heartbeat after consuming alcohol. This discourages heavy drinking, reducing alcoholism rates in this population.
- In contrast, individuals of European descent may have genetic variants that allow them to metabolize alcohol more efficiently, which can contribute to a higher risk of alcohol use disorder.
- These genes affect how quickly alcohol is broken down in the body.
- Nicotine Addiction and CHRNA5 Gene –
- Research has found that African Americans are more likely to carry genetic variants of the CHRNA5 gene, which influences nicotine dependence. This may explain why smoking rates and difficulty quitting smoking are higher in some African American populations.
- Research has found that African Americans are more likely to carry genetic variants of the CHRNA5 gene, which influences nicotine dependence. This may explain why smoking rates and difficulty quitting smoking are higher in some African American populations.
- Opioid Addiction and OPRM1 Gene –
- Variants of the OPRM1 gene, which influence opioid sensitivity, are more common in certain populations. Native Americans and some European groups may have a higher genetic predisposition to opioid addiction.
- Variants of the OPRM1 gene, which influence opioid sensitivity, are more common in certain populations. Native Americans and some European groups may have a higher genetic predisposition to opioid addiction.
Gender Differences in Addiction Genetics
Men and women experience addiction differently due to both biological and genetic factors.
- Men
- More likely to use drugs for pleasure or social reasons.
- Tend to develop addiction more slowly but have a harder time quitting.
- Genetic studies show that men may have higher levels of dopamine release, reinforcing drug-seeking behavior.
- More likely to use drugs for pleasure or social reasons.
- Women
- More likely to use drugs due to stress, trauma, or emotional distress.
- Tend to develop addiction faster than men, a phenomenon known as “telescoping”.
- Estrogen affects dopamine pathways, which may explain why women experience stronger cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- More likely to use drugs due to stress, trauma, or emotional distress.
Understanding these differences can help develop targeted addiction prevention and treatment programs based on ethnicity and gender.
Breakthroughs in Genetic Research for Addiction Treatment
Advances in genetic research have opened new possibilities for personalized addiction treatment. Scientists are exploring how genetic testing can help determine the most effective treatments for individuals based on their genetic makeup.
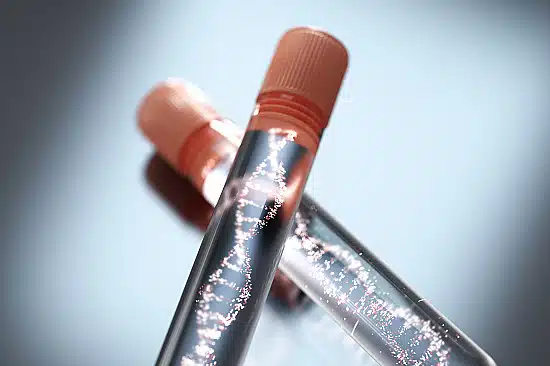
Genetic Testing for Addiction Risk
Genetic testing can help identify individuals at higher risk for addiction before they start using substances. Some companies now offer genetic tests that analyze DNA to predict addiction susceptibility based on inherited traits. This information can be used for early intervention and prevention strategies.
Personalized Medication Based on Genetics
Genetic research is paving the way for precision medicine in addiction treatment. Some examples include:
- Opioid Addiction Treatment (Naltrexone & Methadone)
- The OPRM1 gene influences how individuals respond to opioid medications.
- Some people metabolize methadone faster due to genetic differences, requiring adjusted dosages for effective treatment.
- The OPRM1 gene influences how individuals respond to opioid medications.
- Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) Treatment
- The effectiveness of naltrexone (a medication used to treat alcohol addiction) depends on genetic variations in opioid receptors.
- People with a specific OPRM1 gene variant may respond better to naltrexone, while others may require different medications.
- The effectiveness of naltrexone (a medication used to treat alcohol addiction) depends on genetic variations in opioid receptors.
- Nicotine Addiction Treatment
- Bupropion and varenicline are two medications used for quitting smoking. Genetic testing can help determine which medication will work best based on a person’s CHRNA5 gene variant.
- Bupropion and varenicline are two medications used for quitting smoking. Genetic testing can help determine which medication will work best based on a person’s CHRNA5 gene variant.
Future of Genetic Research in Addiction Treatment
Scientists are working on gene therapy and epigenetic drugs that could modify addiction-related genes to reduce the risk of substance use disorders. While this research is still in its early stages, it holds promise for preventing and treating addiction more effectively in the future.
How to Use These Sections in Your Article
You can add these three sections in different parts of your article to enhance its depth and comprehensiveness. Here’s a possible placement:
- “The Role of Neurotransmitters in Addiction and Genetics” → After the section on “Genes Linked to Addiction.”
- “Ethnic and Gender Differences in Genetic Addiction Risk” → After the section on “Family History and Addiction.”
- “Breakthroughs in Genetic Research for Addiction Treatment” → Before the conclusion, after discussing current treatment options.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Conclusion
Drug addiction is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. While individuals with a family history of addiction have a higher risk, addiction is not inevitable. Through early intervention, education, healthy coping strategies, and support systems, individuals can mitigate their risk.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, seek help today. Call the Addiction Helpline America hotline at (844) 561-0606 for professional support and resources.
Can drug addiction be inherited?
What genes are linked to addiction?
If my parents were addicts, will I be too?
How does genetic research help in addiction treatment?
Can addiction be prevented if it runs in my family?
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.