Understanding the Search for a Schizophrenia Cure
When a loved one is diagnosed with schizophrenia, many people search for a cure for schizophrenia. While there is currently no cure, it is a highly treatable condition. With the right combination of medication, therapy, and support, many people with schizophrenia live fulfilling, independent lives. Recovery is possible, and early intervention leads to better long-term outcomes.
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition affecting approximately 1 in 300 people worldwide. It impacts how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, sometimes making it hard to distinguish reality from hallucinations. The illness is best understood as a lifelong condition requiring ongoing management, much like diabetes or high blood pressure. Encouragingly, research shows that a significant number of people who receive treatment experience major symptom reduction, allowing them to live relatively normal lives.
This article will guide you through modern treatments and the promising research in the search for a cure for schizophrenia. At Addiction Helpline America, we connect individuals and families with comprehensive care for mental health and co-occurring addiction issues. We’re here to provide clear information and compassionate support to help you steer the path to recovery.
Basic cure for schizophrenia glossary:
Understanding Schizophrenia: A Complex Brain Disorder
Schizophrenia is a complex medical illness that affects brain function, changing how a person thinks, feels, and perceives the world. It is not a character flaw or a choice, but a treatable condition. Common myths about multiple personalities or dangerousness are inaccurate; the condition is about disruptions in the brain’s communication network.
Symptoms and Presentation
Understanding the symptoms is key to recognizing why the search for a cure for schizophrenia is so important. Symptoms are grouped into three categories.
Positive symptoms are experiences added to a person’s reality. These include hallucinations, such as hearing voices or seeing things that aren’t there, and delusions, which are firmly held false beliefs (e.g., believing one is being persecuted or has special powers). These experiences feel completely real to the individual. Disorganized thinking can appear as jumbled speech, while behavior may become agitated or unpredictable.
Negative symptoms involve the absence of normal behaviors. This can include a flat affect (reduced emotional expression), loss of motivation, lack of pleasure in daily activities, and social withdrawal. These symptoms are often mistaken for laziness or depression but are a core part of the illness. A related challenge is anosognosia, a lack of insight into one’s own illness, which can make accepting treatment difficult.
Cognitive symptoms affect information processing. Individuals may struggle with concentration, memory, planning, and problem-solving, making everyday tasks difficult. Many people experience a prodromal period with subtle changes like declining grades or social withdrawal before the illness fully develops. Symptoms typically emerge in the early 20s for men and mid-20s to early 30s for women.
Causes and Risk Factors
There is no single cause of schizophrenia, which is why a cure for schizophrenia is elusive. It’s believed to develop from a combination of factors.
- Genetics: A family history significantly increases risk. Someone with a parent or sibling with schizophrenia is more than six times more likely to develop it, but genetics are not destiny.
- Brain Chemistry and Structure: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like dopamine and glutamate play a role. Issues with brain development before birth or during childhood can also contribute.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors like prenatal exposure to viruses, birth complications, or significant childhood stress can increase risk in vulnerable individuals.
- Substance Use: Using marijuana during adolescence is a significant risk factor. Other substances can also trigger or worsen symptoms, highlighting the need for integrated treatment for co-occurring disorders.
How Schizophrenia is Diagnosed
There is no single blood test or brain scan for schizophrenia. Diagnosis is made by a mental health professional through a comprehensive evaluation.
A psychiatrist will conduct a detailed interview about symptoms, experiences, and family history. The symptoms are compared to criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). A diagnosis requires at least two key symptoms (like delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech) for a significant time over one month, with continuous signs of disturbance for at least six months.
Ruling out other conditions is crucial. Psychotic symptoms can be caused by bipolar disorder, depression, certain medications, or medical issues like a brain tumor. A physical exam, blood work, and sometimes brain imaging (MRI or CT scan) are used to exclude these other causes. A diagnosis is the first step toward getting the right treatment and support. At Addiction Helpline America, we help families steer this journey and find the comprehensive care they need.
The Comprehensive Treatment Landscape: Managing Symptoms Effectively
While there is no cure for schizophrenia, effective management is entirely possible. The goal is to reduce symptoms and help people reclaim their lives. This requires lifelong management, similar to other chronic health conditions. A coordinated care team—including a psychiatrist, psychologist, social worker, and case manager—is essential for creating an individualized treatment plan.
The Role of Medication
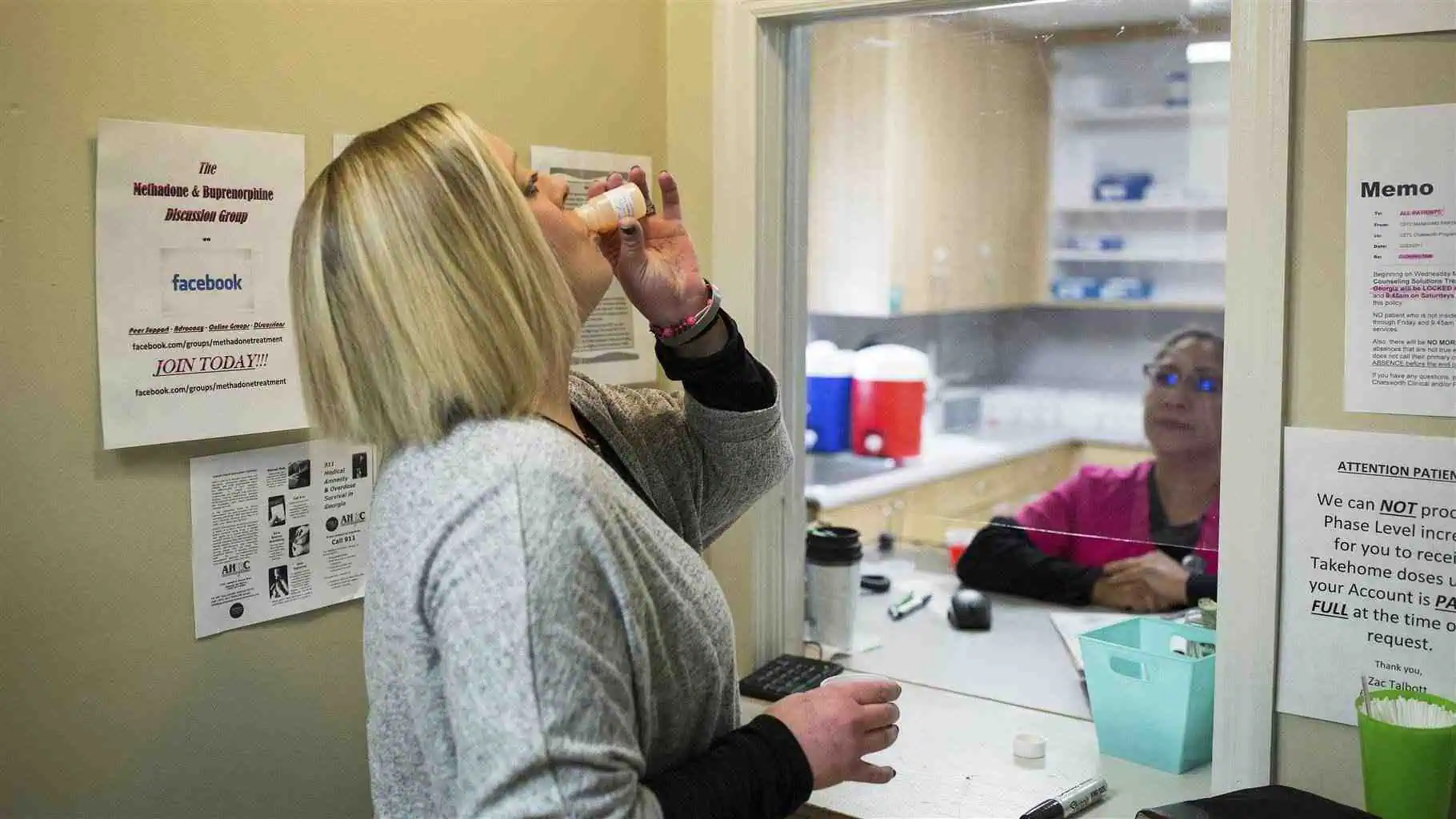
Antipsychotic medications are the cornerstone of treatment, primarily targeting disruptive symptoms like hallucinations and delusions by affecting brain chemicals like dopamine and serotonin.
- First-generation (typical) antipsychotics, developed in the 1950s, are effective for positive symptoms but can cause movement-related side effects, including a risk of tardive dyskinesia (involuntary, repetitive movements).
- Second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics, developed in the 1990s, generally have a lower risk of movement side effects but can cause weight gain and metabolic changes. Clozapine is a uniquely effective option for treatment-resistant schizophrenia but requires careful blood monitoring.
- Long-acting injectable antipsychotics are administered every few weeks or months, offering a convenient alternative to daily pills.
Finding the right medication and dosage takes time and open communication with your doctor about side effects. It’s crucial to continue taking medication even when feeling better, as stopping can cause a relapse. While not a cure for schizophrenia, these drugs are powerful tools for symptom control.
The Power of Psychosocial Interventions
Therapy helps individuals build coping skills and improve daily functioning. These interventions work alongside medication to support recovery.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for psychosis (CBTp) teaches strategies to manage persistent symptoms and regain a sense of control.
- Family therapy educates loved ones and improves communication, leading to better outcomes for everyone.
- Social skills training helps steer social situations, while vocational rehabilitation assists with finding and keeping employment.
- Assertive Community Treatment (ACT) teams provide proactive, hands-on support in the community to prevent crises.
- Other helpful therapies include supportive psychotherapy, Cognitive Improvement Therapy (CET) for cognitive deficits, arts therapy, and peer support groups.
Addressing Co-Occurring Conditions
Schizophrenia often co-occurs with other health issues. Integrated treatment is key.
The link between schizophrenia and substance use disorders is strong. Substances like marijuana can worsen symptoms or trigger the illness in vulnerable people. Integrated programs that treat both mental health and addiction simultaneously are most effective. If you need help, resources like Substance Use Disorder Treatment, Opioid Addiction Treatment Options, and the Alcohol Addiction Helpline are available. Understanding Why People Become Addicted to Drugs can also be helpful.
People with schizophrenia also have a higher risk of physical health problems like diabetes and heart disease, as well as other mental health conditions like PTSD and depression. Comprehensive care addresses all aspects of a person’s health. At Addiction Helpline America, we help you find programs that provide this level of integrated care.
Breakthroughs on the Horizon: The Quest for a Cure for Schizophrenia
The search for a cure for schizophrenia is more active than ever. Scientists are making exciting progress in understanding the brain’s neurobiology and circuit dysfunction, with a growing emphasis on early intervention to prevent the full onset of the illness. For decades, all medications worked by targeting dopamine, but researchers are now exploring entirely new pathways.
A New Class of Medication: Beyond Dopamine
For over 50 years, antipsychotics have focused on dopamine and serotonin pathways. In 2024, the FDA approved Cobenfy (xanomeline and trospium chloride), the first new pharmacological approach in decades that does not rely on these traditional pathways. Instead, it works on the cholinergic neurotransmitter system by activating muscarinic receptors in the brain.
This is a major leap forward. Clinical trials show Cobenfy can address positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms—all three major categories. This is significant because traditional antipsychotics often fail to improve negative and cognitive symptoms. Furthermore, Cobenfy has a low incidence of common side effects like sleepiness, weight gain, and abnormal motor movements, offering hope to many who have struggled with existing treatments.
Other Emerging Drug Therapies
Researchers are exploring several other promising pathways:
- NMDA Receptor Modulation: People with schizophrenia often have lower levels of D-serine, a chemical important for cognitive function. Drugs like Luvadaxistat aim to boost D-serine levels to improve cognitive and behavioral symptoms.
- Sodium Benzoate: A new form called Ω-NaBen (Omega-NaBen) is being investigated as an add-on therapy to improve positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms, even for treatment-resistant patients.
- Other Targets: Scientists are also investigating GABAergic and glutamatergic pathways, trace amine receptors, and PDE10A inhibitors, each representing a different approach to treatment.
This table compares the different treatment types:
| Treatment Type | Primary Mechanism | Key Symptom Targets | Notable Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional (First-Gen Antipsychotics) | Dopamine receptor blockade (D2) | Primarily positive symptoms (hallucinations, delusions) | Motor side effects (tardive dyskinesia, muscle spasms), sedation, weight gain |
| Atypical (Second-Gen Antipsychotics) | Dopamine (D2) and Serotonin (5-HT2A) receptor modulation | Positive, some negative symptoms | Metabolic issues (weight gain, diabetes risk), sedation, some motor effects |
| Cobenfy (Xanomeline/Trospium) | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation (brain), blockade (body) | Positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms | Low incidence of traditional antipsychotic side effects (less weight gain, sleepiness) |
| Luvadaxistat (DAAO inhibitor) | Increases D-serine, modulating NMDA receptors | Primarily cognitive symptoms | Research ongoing, specific side effects still under evaluation |
| Ω-NaBen (Sodium Benzoate) | NMDA receptor improvement (indirectly via D-serine) | Positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms | Research ongoing, improved absorption aims to reduce side effects |
The Future of Finding a Schizophrenia Cure
Today’s research is laying the groundwork for future breakthroughs. Genetic research may lead to personalized, gene-based therapies. The search for reliable biomarkers could allow for earlier diagnosis and more targeted treatment. Neurostimulation techniques like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are also being explored for treatment-resistant cases.
While a definitive cure for schizophrenia is still on the horizon, the pace of findy is accelerating. This research represents tangible hope for treatments that could fundamentally change the course of the illness. At Addiction Helpline America, we stay informed about these developments to connect you with the most effective treatments available.
Living a Fulfilling Life: Prognosis, Recovery, and Support
When facing a schizophrenia diagnosis, it’s natural to wonder about the future. The answer is that a good life is still possible. While there is no cure for schizophrenia, meaningful recovery is within reach for many. Schizophrenia is a lifelong condition with cycles of symptoms, which is why continuous treatment is vital, even during periods of wellness. Stopping treatment can lead to a relapse.
Encouragingly, research shows that with treatment, a large percentage of people with schizophrenia experience significant symptom reduction, allowing them to live independently, maintain relationships, and hold jobs. Without treatment, however, the condition can lead to severe complications and an increased risk of suicide. If you or a loved one are having suicidal thoughts, please get help immediately. You can call or text 988 to reach the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline 24/7. For medical emergencies, always call 911.
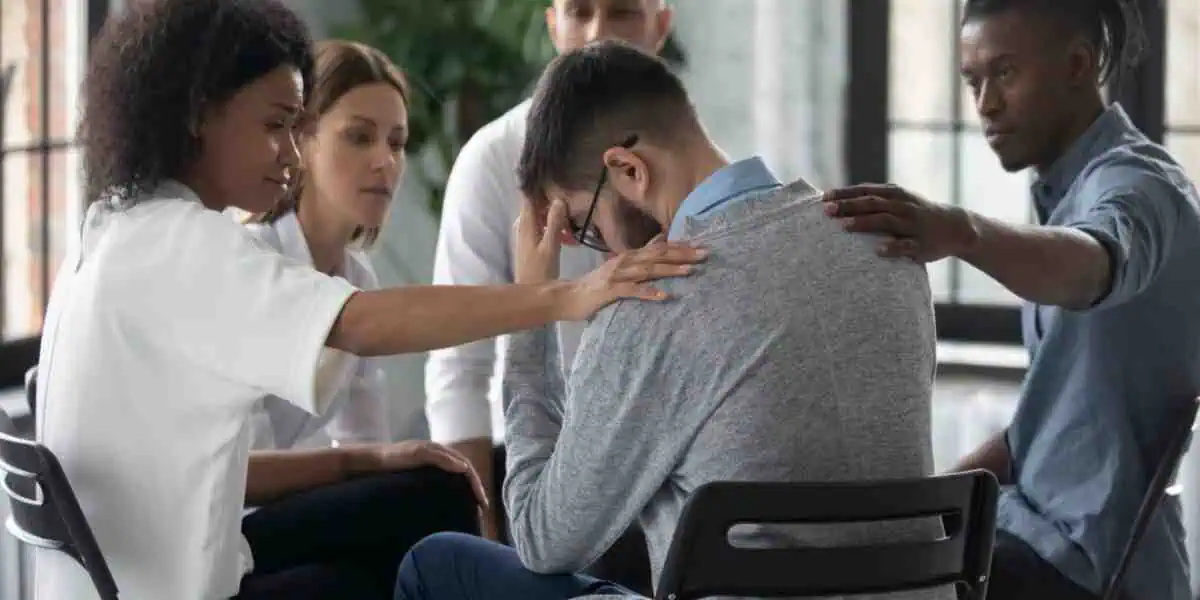
Building a Strong Support System
No one should face schizophrenia alone. A strong support system is crucial for recovery.
- Family and friends can provide practical help and emotional encouragement. Understanding the illness, including anosognosia (a lack of insight), helps families respond with empathy.
- Support groups, like those offered by the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), connect you with peers who share similar experiences.
- Community Mental Health Teams (CMHTs) and Assertive Community Treatment (ACT) programs offer proactive, day-to-day support to manage life’s challenges and prevent crises.
- A crisis plan, created in advance, can outline care preferences during a severe symptom episode. Resources like a Crisis Stabilization Unit provide immediate, specialized support.
Coping Strategies and Self-Care
Daily habits are an essential part of managing schizophrenia and building a fulfilling life.
- Stress management techniques like deep breathing or meditation can help keep symptoms stable.
- A healthy lifestyle, including adequate sleep, a balanced diet, and regular exercise, supports both physical and mental health.
- Avoiding alcohol and drugs is critical, as substance use can worsen symptoms and interfere with medication. For confidential help, consider resources like Anonymous Addiction Help.
- Setting realistic goals with your treatment team builds confidence and momentum.
- Learning about schizophrenia empowers you and your family to be active participants in the recovery process.
At Addiction Helpline America, we’ve seen countless individuals find a path to recovery. With the right support and treatment, living a fulfilling life with schizophrenia is not just possible—it’s a reality for many.
Frequently Asked Questions and Finding Help
When dealing with schizophrenia, you’re bound to have questions. The search for a cure for schizophrenia often leads people to us for answers and hope. Here are some common concerns.
Can schizophrenia be prevented?
Currently, there is no guaranteed way to prevent schizophrenia. However, you can take steps to reduce risk. Early intervention is key; seeking help for early warning signs (the prodromal period) can improve long-term outcomes. Avoiding substance use, especially marijuana during adolescence, is also an important preventive measure, particularly for those with a family history of the illness.
What happens if schizophrenia is left untreated?
Untreated schizophrenia typically worsens over time, leading to severe complications. Symptoms intensify, and the person may lose touch with reality, making it nearly impossible to function. The risk of social isolation, homelessness, and suicide increases significantly. This is why seeking help is so critical. If you or someone you know is in crisis, please call or text 988 to reach the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline. For immediate medical emergencies, call 911.
Is there a natural cure for schizophrenia?
There is no scientific evidence for a natural cure for schizophrenia. However, some complementary approaches can support overall well-being when used alongside evidence-based medical care. These may include omega-3 fatty acids, meditation, or acupuncture. Always discuss these options with your doctor first to ensure they are safe and do not interfere with your primary treatment plan.
Finding Personalized Treatment
While a definitive cure for schizophrenia doesn’t exist yet, effective management and a fulfilling life are absolutely possible. Promising research and new medications like Cobenfy are offering more hope than ever before. Recovery requires commitment, support, and personalized care—but it is achievable.
If you or a loved one are seeking support for schizophrenia or co-occurring substance use disorders, you don’t have to do it alone. At Addiction Helpline America, we specialize in helping people steer the complexities of mental health treatment. We offer free, confidential, personalized guidance to help you find the right recovery program from our extensive network of treatment centers.
We can connect you with quality care nationwide, in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. You deserve support that understands your whole situation. Get professional help for mental health today, and let us help you take the first step toward a stable and meaningful life. Recovery is possible, and we’re here to help you find your path.
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.