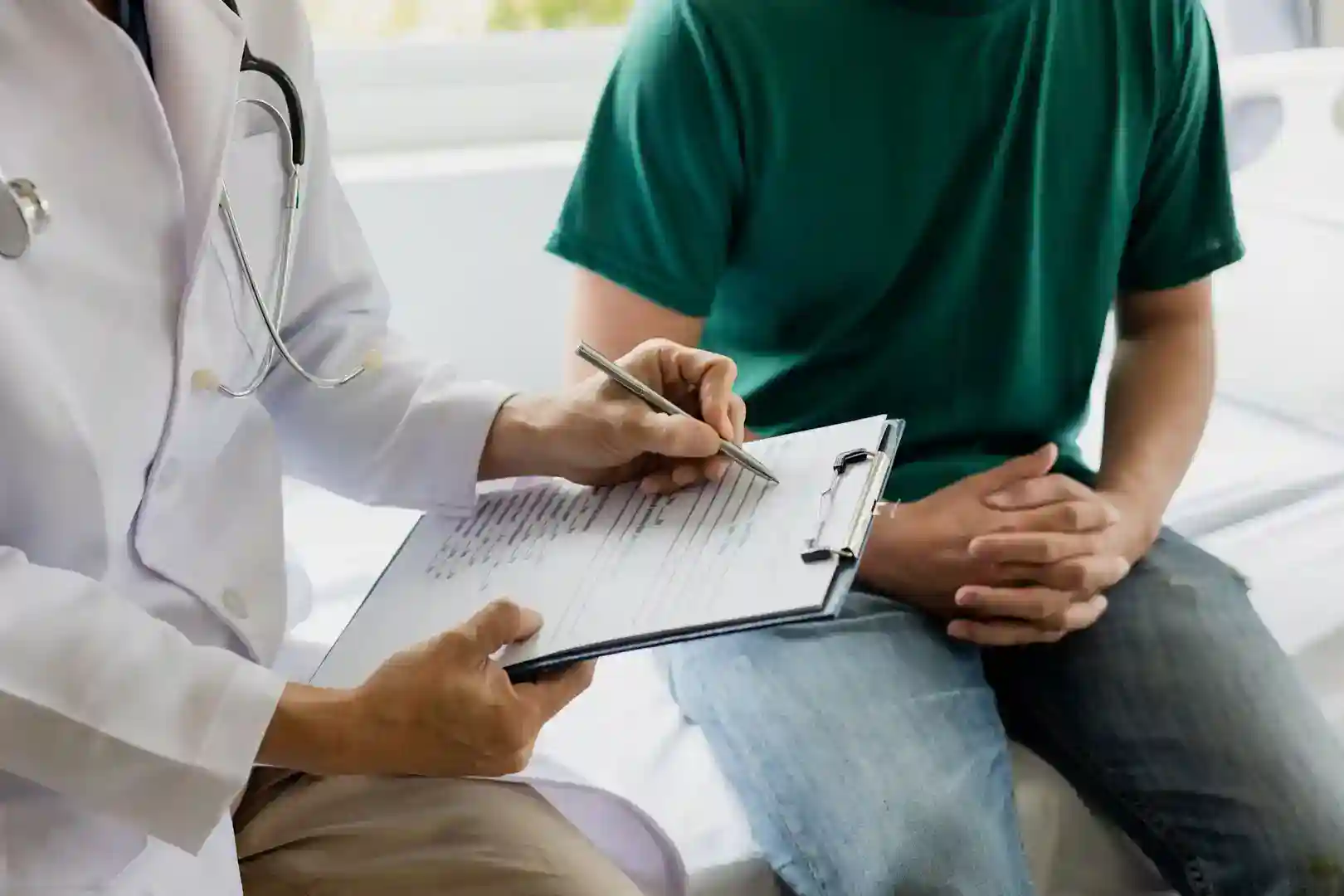
Understanding Meloxicam: A Prescription NSAID for Pain Relief
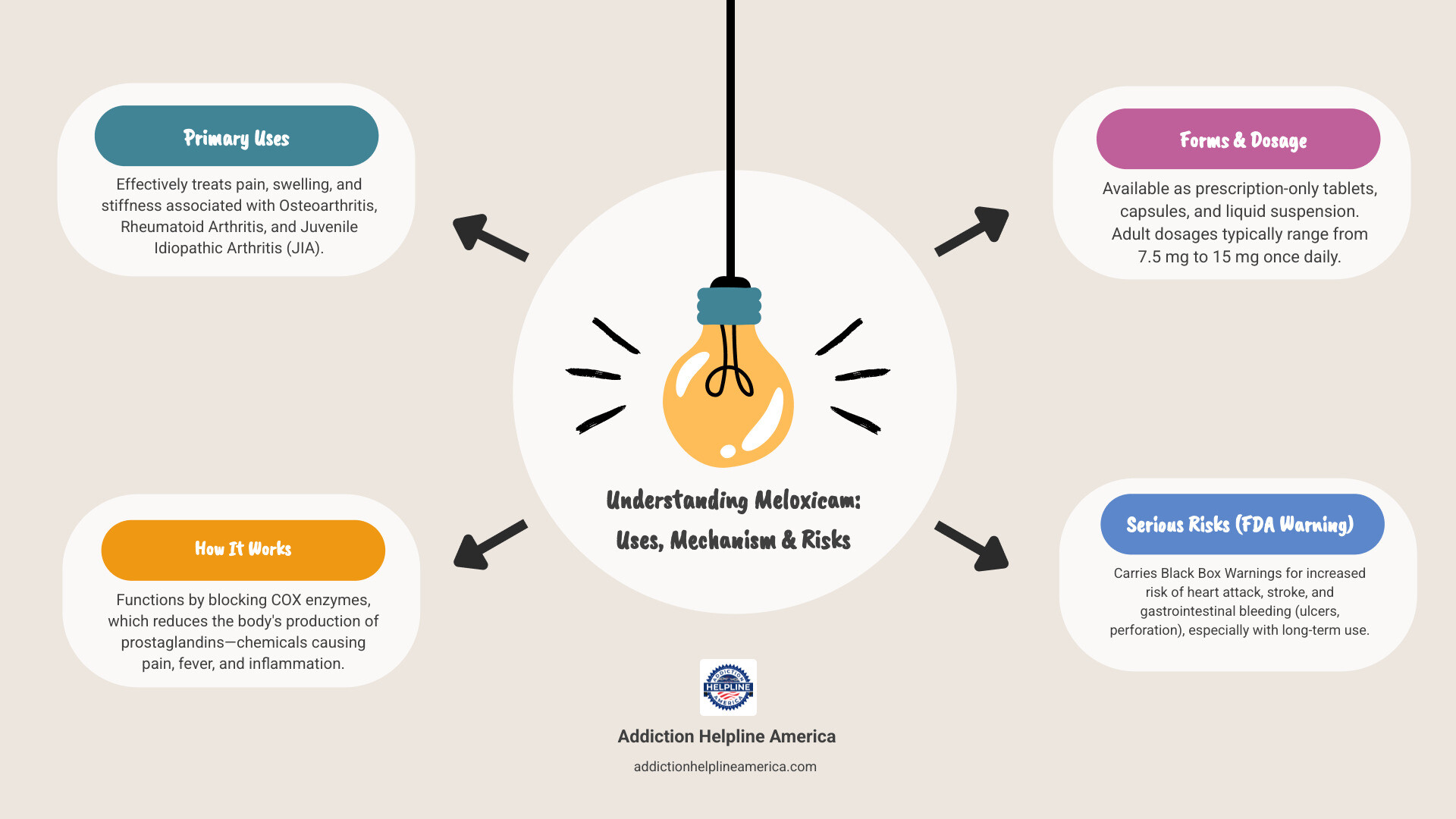
What is meloxicam used for? Meloxicam is a prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, swelling, and stiffness from arthritis, including:
- Osteoarthritis – arthritis caused by breakdown of joint lining
- Rheumatoid arthritis – arthritis caused by inflammation of joint lining
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) – in children 2 years and older
It works by blocking prostaglandins—chemicals causing pain, fever, and inflammation. While not a cure for arthritis, it effectively manages symptoms when taken as prescribed.
Important note: Meloxicam is a prescription-only medication available in tablets, capsules, liquid suspension, and disintegrating tablets. The typical adult dose is 7.5 mg to 15 mg once daily.
However, meloxicam has serious risks. The FDA issued black box warnings for increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and gastrointestinal bleeding, especially with long-term use or in patients with heart conditions. With over 9 million prescriptions annually, understanding its benefits and dangers is crucial.
At Addiction Helpline America, we help individuals and families steer complex medication concerns, including guiding people toward safer pain management options when prescription drugs become problematic.
What is Meloxicam and How Does It Work?
If you’ve been prescribed meloxicam, understanding how it works is key to using it safely.
What Type of Drug is Meloxicam?
Meloxicam belongs to a group of medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs. Unlike over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen, meloxicam is prescription-only.
Meloxicam requires a prescription because it’s used for chronic conditions like arthritis and carries risks that need medical supervision, especially with regular use.
As an NSAID, meloxicam’s main job is reducing pain and inflammation. It manages your symptoms—it doesn’t cure the underlying condition.
For more detailed medical information about meloxicam’s classification and uses, you can check out MedlinePlus.
The Mechanism of Action: Relieving Pain and Inflammation
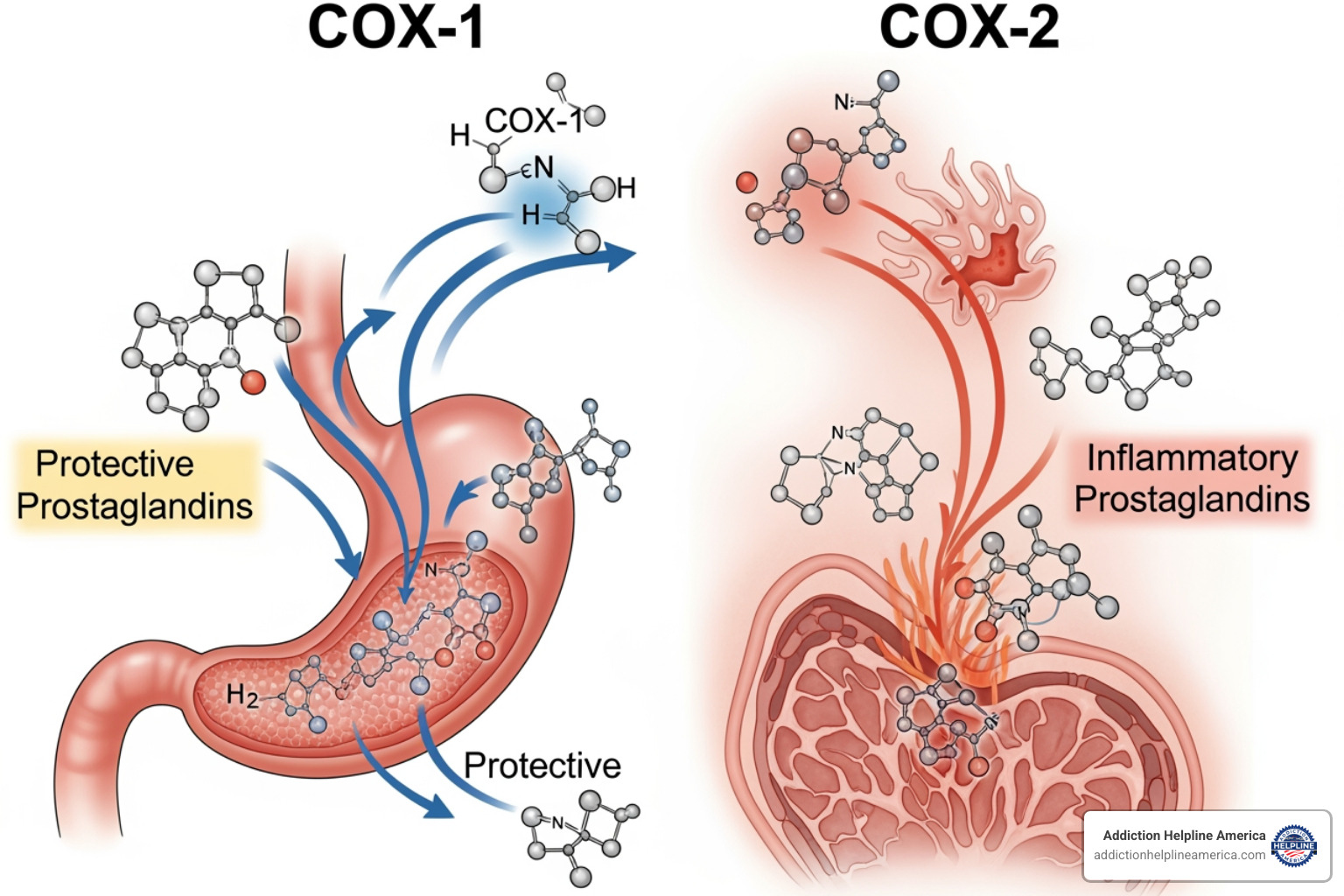
Your body produces chemicals called prostaglandins in response to injury or inflammation. They act as an alarm system, causing pain, fever, and swelling. In chronic conditions like arthritis, this process causes persistent discomfort.
Meloxicam works by blocking enzymes called COX-1 and COX-2 (cyclo-oxygenase enzymes), which are the factories that produce prostaglandins. When meloxicam shuts down these factories, your body makes fewer prostaglandins, resulting in less pain, lower fever, and reduced inflammation.
Meloxicam is more selective in blocking COX-2 over COX-1. Since COX-1 helps protect the stomach lining and COX-2 primarily causes inflammation, this selectivity may lead to fewer stomach issues compared to some other NSAIDs.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
That said, meloxicam still affects both enzymes, which is why stomach issues remain a real concern.
Understanding what is meloxicam used for and how it works helps you have better conversations with your doctor about whether it’s the right choice for managing your pain.
What is Meloxicam Used For?
Here’s a look at what meloxicam is used for in medical practice.
Approved Conditions: What is Meloxicam Used For?
Meloxicam is commonly prescribed to manage the daily struggle of arthritis. It’s a go-to option for doctors treating specific joint conditions involving chronic pain and inflammation.
Osteoarthritis is the most common reason people take meloxicam. It is a “wear-and-tear” condition where joint cartilage breaks down. Meloxicam helps reduce the associated pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks joint linings, causing severe inflammation. Meloxicam eases these symptoms but doesn’t fix the underlying immune issue.
For younger patients, meloxicam is FDA-approved to treat juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children aged 2 and older. This medication can help children with JIA return to normal activities by reducing their pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness.

It’s important to know that meloxicam is not a cure for arthritis. It doesn’t reverse damage or stop disease progression. Instead, it improves quality of life and mobility by making the condition more bearable.
Available Forms and Typical Dosages
Meloxicam comes in several forms to suit different patient needs.
- Oral tablets (7.5 mg and 15 mg) and oral capsules (5 mg and 10 mg) are common for adults.
- An oral suspension (liquid) is available for those who have trouble swallowing pills.
- Disintegrating tablets dissolve on the tongue without water.
Doctors follow a key principle: use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration to minimize side effects.
For adults with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, treatment usually starts at 7.5 mg once daily, with a maximum of 15 mg daily. The capsule form for osteoarthritis may start at 5 mg daily, with a maximum of 10 mg.
For children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the dose is based on body weight, typically 0.125 mg/kg once daily, not to exceed 7.5 mg per day. Meloxicam is not recommended for children under 2.
Patients on hemodialysis have a maximum dose of 7.5 mg daily. Different meloxicam formulations may not be interchangeable at the same milligram strength due to absorption differences. Always use the specific form your doctor prescribed.
At Addiction Helpline America, we know understanding your medication is key to safety. These are general guidelines; your provider will determine the right dose for your unique situation.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Warnings
While meloxicam can be effective for arthritis pain, it’s a powerful medication with risks that require your full attention.
Common and Serious Side Effects
Many people tolerate meloxicam well, but common side effects can occur, especially initially. These include stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, heartburn, dizziness, headaches, flu-like symptoms, or a mild skin rash.
These side effects are often manageable and may decrease over time. If they persist or interfere with daily life, contact your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
However, some side effects are serious and require immediate medical attention.
- Signs of a heart attack or stroke: Chest pain, shortness of breath, or sudden weakness on one side of the body.
- Signs of internal bleeding: Black, tarry stools or vomiting blood (or what looks like coffee grounds).
- Severe skin reactions: Blistering, peeling, or intense rashes with fever can be life-threatening.
- Kidney or fluid retention issues: Unexplained weight gain or swelling in the ankles and legs.
- Liver problems: Yellowing skin or eyes, or severe upper stomach pain.
- Serious allergic reaction: Difficulty breathing, hoarseness, or swelling of your face or throat.
If you experience any of these serious symptoms, stop taking meloxicam and get immediate medical help. Report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch or 1-800-FDA-1088.
FDA Black Box Warnings and Long-Term Risks
Meloxicam has two significant FDA Black Box Warnings, the agency’s most serious alert, highlighting major risks.

The cardiovascular risk: Meloxicam can increase the risk of a fatal heart attack or stroke. This risk can appear early in treatment and increases with higher doses and longer use, especially for those with existing heart disease. It should not be used around the time of heart bypass surgery (CABG).
The gastrointestinal risk: Meloxicam can cause fatal stomach or intestinal bleeding, ulcers, or perforation (a hole in the stomach or intestine). These can occur without warning. The risk is higher for older adults, those with a history of ulcers, smokers, regular alcohol drinkers, or those taking other specific medications.
Long-term use for chronic conditions amplifies these risks. The longer you take meloxicam, the greater the danger. Regular monitoring by your doctor, including potential blood and urine tests, is essential to catch problems early.
At Addiction Helpline America, we understand these complex decisions. If you’re concerned about your meloxicam use or need guidance on safer pain management alternatives, we can help you explore your options.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Important Precautions and Drug Interactions
Taking meloxicam requires awareness of how it might affect you based on your health and other medications. Certain people must be extra cautious, and interactions with other substances can be dangerous.
Who Should Be Cautious When Taking Meloxicam?
Have an honest conversation with your doctor if you fall into any of these categories:
- 65 or older: Elderly patients face a higher risk of stomach bleeding, kidney problems, and heart complications. Doctors typically prescribe a lower dose and monitor them more closely.
- Pregnant or planning pregnancy: After 20 weeks of pregnancy, NSAIDs can harm a baby’s kidneys. After 30 weeks, they can cause serious fetal heart problems. Ask your doctor about safer alternatives.
- Breastfeeding: It’s unknown how much meloxicam passes into breast milk. Discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
- Trying to conceive: Meloxicam can cause a reversible delay in ovulation and may decrease sperm count in men. Discuss this with your doctor before starting.
- Have pre-existing health conditions: Meloxicam can worsen heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney problems, or liver disease. It can trigger severe reactions in those with aspirin-sensitive asthma and increases bleeding risk for those with a history of stomach ulcers or bleeding disorders.
What is Meloxicam Used For and How Does It Interact with Other Substances?
Meloxicam can interact dangerously with numerous medications and substances. Provide your doctor and pharmacist with a complete list of all medications, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and supplements you take.
Key interactions include:
- Other NSAIDs or aspirin: Combining these with meloxicam dramatically increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin) and certain antidepressants (SSRIs/SNRIs): These combinations increase the risk of serious bleeding.
- Blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers): Meloxicam can reduce their effectiveness.
- Diuretics (water pills): The combination can reduce diuretic effectiveness and increase kidney risk.
- Lithium and methotrexate: Meloxicam can increase levels of these drugs in the blood, leading to toxicity.
- Cyclosporine and pemetrexed: These combinations increase the risk of kidney damage and toxicity, respectively.
Alcohol and tobacco also pose risks. Drinking alcohol while taking meloxicam significantly increases your risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Smoking also increases this risk, so quitting is worth considering.
At Addiction Helpline America, we’ve helped thousands steer these complexities, especially when prescription medication use becomes problematic. You don’t have to figure this out alone.
Frequently Asked Questions about Meloxicam
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about using meloxicam safely and effectively.
What should I do if I miss a dose of meloxicam?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one. Never take a double dose to make up for a missed one, as this increases the risk of side effects. Resume your regular schedule with the next dose.
If you frequently miss doses, talk to your doctor or pharmacist about strategies to stay on track, like using a pill organizer or setting a daily alarm.
How should meloxicam be stored and disposed of?
Storage: Keep meloxicam in its original, tightly closed container at room temperature (68°F to 77°F), away from heat and moisture. The bathroom is not an ideal storage spot. Always keep medications out of sight and reach of children. For more tips, visit Up and Away.
Disposal: Do not flush unneeded medication unless the label instructs you to. The best option is a medicine take-back program. Your pharmacist can help you find one, or you can find guidance on proper disposal at this resource.
Is meloxicam a narcotic or an opioid?
To be clear: No, meloxicam is not a narcotic or an opioid.
Meloxicam is an NSAID that works by reducing inflammation at the source. Opioids work differently, attaching to receptors in the brain to change pain perception, which creates a high risk for addiction.
Meloxicam does not affect the brain’s reward pathways like opioids, so it has a much lower potential for physical dependence and addiction. However, misuse is still possible. Taking more than prescribed, for longer than necessary, or without a therapeutic need can lead to psychological dependence. The FDA advises caution when prescribing it to patients with a history of psychological dependence on other drugs.
Understanding this difference is crucial for safe pain management. At Addiction Helpline America, we’re committed to providing clear information so you can approach your health with confidence.
Conclusion: Using Meloxicam Safely and Seeking Help
We’ve covered what is meloxicam used for, how it works, its dosages, and its significant risks. Meloxicam can be a life-changing medication for those with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis, offering relief from pain, swelling, and stiffness that can restore quality of life.
However, this relief comes with responsibility. The FDA’s Black Box Warnings for heart attack, stroke, and stomach bleeding are genuine risks. Combined with potential drug interactions and special precautions for certain groups, it’s clear that meloxicam requires careful medical supervision.
Using meloxicam requires knowledge and guidance. Be proactive in your care: ask questions, report unusual symptoms immediately, and ensure your entire healthcare team has your complete medical history, including all medications and supplements.
Managing chronic pain is exhausting, and sometimes the line between proper use and problematic patterns can blur. You might find yourself taking more than prescribed or using it in ways not aligned with your doctor’s instructions. These situations are common and human.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
At Addiction Helpline America, we’ve spent years helping thousands of individuals and families steer these exact concerns. We know that asking for help takes courage, and we’re here to meet you exactly where you are—without judgment, with complete confidentiality, and with genuine compassion.
If you or a loved one are struggling with prescription drug misuse, help is available right now. Our team provides free, personalized guidance to help you find the right recovery program or treatment option for your unique situation. We serve individuals across all fifty states and the District of Columbia, connecting you with trusted resources in your community.
Find personalized treatment options today. Whether you’re concerned about your own medication use, worried about a family member, or simply need someone to talk through your options with, we’re here. Let us help you move toward safer pain management and a path to overall well-being. You don’t have to figure this out alone.
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.