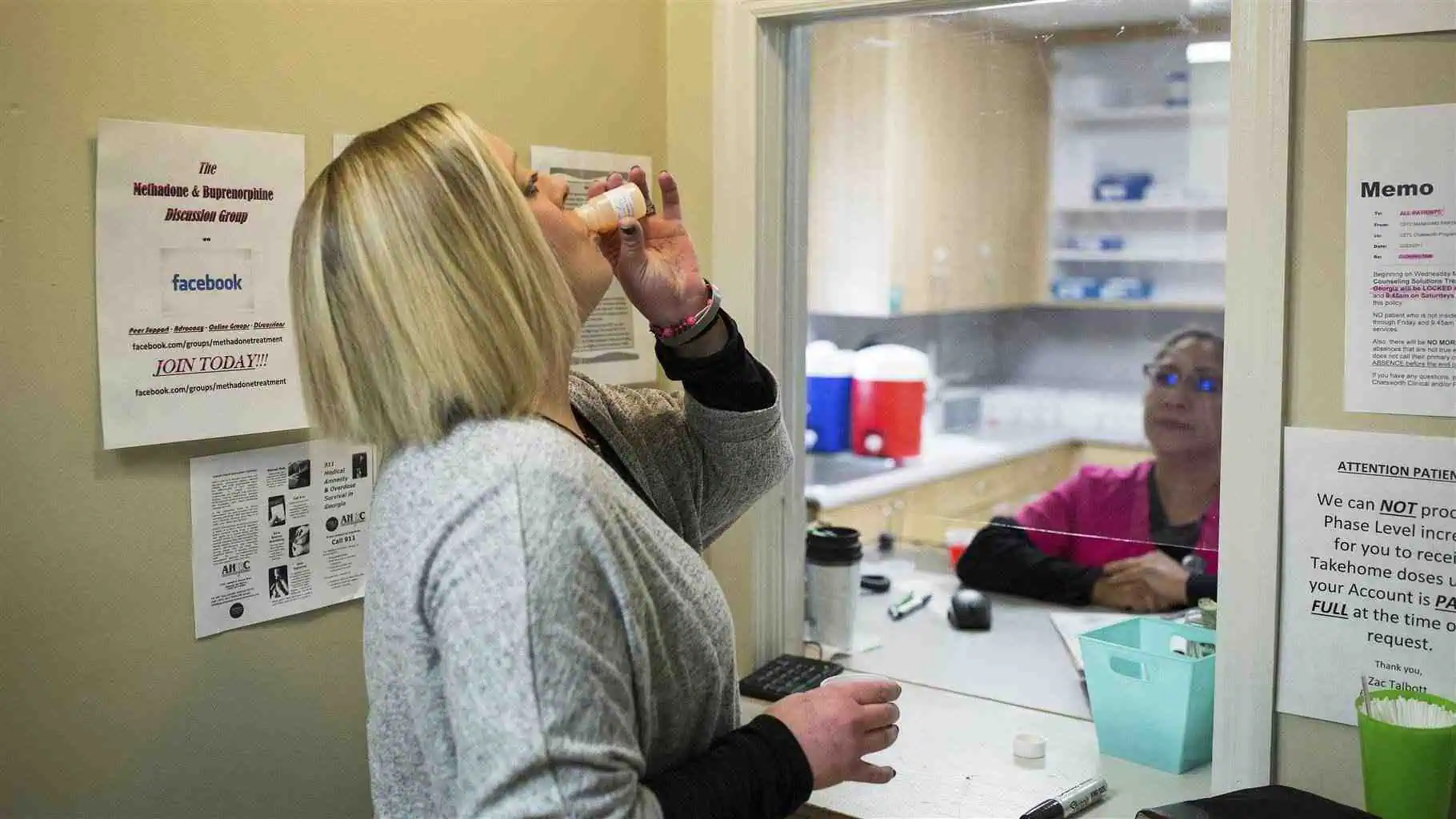
Introduction
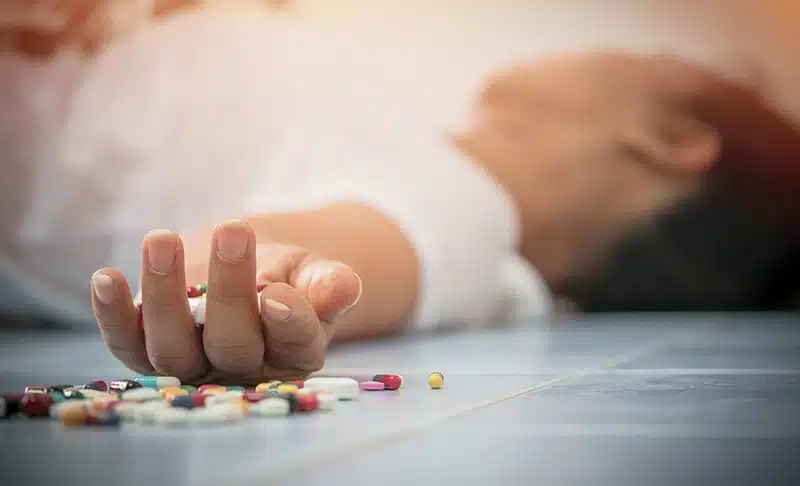
Drug addiction is a pervasive problem that affects millions of individuals across the United States. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), drug addiction, also referred to as substance use disorder (SUD), can have devastating effects on individuals, families, and communities. With a wide range of substances being abused, from prescription medications to illicit drugs, the addiction crisis, particularly concerning drugs in the U.S., continues to grow in scale and impact.
The ongoing opioid epidemic, the rising misuse of prescription drugs, and the continued prevalence of alcohol and nicotine addiction demonstrate the severity of the situation. As we move further into the 21st century, drug addiction, especially related to drugs in the U.S., has become one of the most pressing public health crises in the country.
Understanding Drug Addiction and Its Impact on Drugs in the U.S.
What is Drug Addiction?
Drug addiction, or substance use disorder (SUD), is characterized by an individual’s inability to control their drug use, despite the negative consequences it has on their health, relationships, and overall well-being. Addiction can involve both physical and psychological dependence on a substance, leading to tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and the overwhelming need to continue using the drug.
Drug addiction goes beyond the occasional use of a substance for recreational purposes. It becomes a disorder when individuals continue using despite significant harm to themselves or others. It affects the brain’s reward system, creating a compulsive drive to seek out the substance, even when the behavior is destructive.
Drugs that lead to addiction can be legal (like alcohol and prescription medications) or illegal (such as heroin or cocaine). Regardless of the substance, addiction can have severe consequences for individuals, including impaired cognitive function, health problems, legal issues, and even death due to overdose.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Types of Substances That Cause Addiction
Substances that contribute to addiction in the U.S. include:
- Prescription Drugs: Opioids (e.g., oxycodone, morphine), benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium), and stimulants (e.g., Adderall, Ritalin) are among the most commonly abused prescription medications.
- Illicit Drugs: Cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, and synthetic drugs like fentanyl are examples of illegal substances that cause widespread addiction.
- Alcohol: One of the most commonly abused substances in the U.S., alcohol addiction can lead to severe health consequences, including liver disease, cardiovascular issues, and neurological damage.
- Nicotine: Smoking and vaping continue to be significant contributors to addiction-related health problems in the U.S., including lung cancer, respiratory failure, and heart disease.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Some individuals misuse over-the-counter medications, such as cough syrup, to achieve a high. The active ingredients in these medications, like dextromethorphan (DXM), can be abused for their hallucinogenic effects.
The Statistics of Drug Addiction in the U.S.
Prevalence of Drug Addiction in the U.S.
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), millions of Americans struggle with substance use disorders each year. The following statistics provide a snapshot of drug addiction in the U.S.:
- Approximately 46.3 million adults aged 18 or older had a substance use disorder in 2021, representing 16.5% of the adult population. This figure includes addiction to alcohol, prescription drugs, illicit drugs, and nicotine.
- Over 10 million Americans misused prescription opioids in 2020, contributing to the opioid epidemic in the country. The misuse of opioids continues to be a major public health challenge, leading to a high number of overdose deaths.
- Substance use disorders related to alcohol affected approximately 28.3 million adults in 2021, making alcohol addiction the most prevalent addiction in the U.S. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) states that alcohol is the most widely used substance in the country, contributing to a range of health issues and social consequences.
- Over 100,000 drug overdose deaths occurred in 2021, a staggering figure that includes deaths from opioids, stimulants, and other substances. These deaths highlight the urgent need for intervention and prevention efforts.
- Fentanyl-related deaths have risen dramatically in recent years, with fentanyl accounting for nearly 70% of all drug overdose deaths in the U.S. This powerful synthetic opioid is often mixed with other drugs, such as heroin and cocaine, increasing the risk of overdose and death.
These figures highlight the scope of the drug addiction crisis in the U.S. The impact of addiction is not only felt by individuals but also by their families, communities, and healthcare systems. The opioid crisis, in particular, has led to overwhelming challenges for both public health agencies and law enforcement.
Age Demographics of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction affects people of all ages, but certain age groups are more vulnerable to substance use disorders:
- Young Adults (18-25): This group experiences the highest rate of substance use, with a significant number struggling with binge drinking, marijuana use, and prescription drug misuse. Research shows that early use of substances can increase the risk of developing a long-term addiction.
- Adults (26-49): Many adults in this age group battle opioid addiction, alcohol dependence, and stimulant abuse. Work-related stress, family responsibilities, and financial pressures can often trigger or exacerbate substance use issues in this demographic.
- Older Adults (50+): While the rates are lower in older adults, substance use disorders, particularly alcohol addiction and misuse of prescription medications, are growing concerns among this demographic. Older adults may use substances to cope with the physical and emotional challenges that come with aging, such as chronic pain, isolation, and mental health issues.
It’s essential to address the specific needs of each age group when designing prevention and treatment programs. Tailoring interventions to the unique challenges faced by different generations can help to improve outcomes and reduce the overall burden of addiction.
Contributing Factors to Drug Addiction
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Research has shown that both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of addiction. Individuals with a family history of addiction are at a higher risk of developing a substance use disorder themselves. Genetics can influence how the brain responds to certain substances, making some individuals more prone to addiction.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to substance use in childhood, peer pressure, and stress, can further increase the likelihood of addiction. Growing up in an environment where substance use is normalized, or being exposed to drugs at a young age, can increase an individual’s chances of developing an addiction later in life.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Mental Health and Trauma
Mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), are often co-occurring with addiction. People may turn to drugs and alcohol as a means of self-medication to cope with emotional pain or to numb feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or anxiety. Trauma, especially early childhood trauma, can also increase the risk of developing substance use disorders later in life.
Addressing mental health conditions alongside addiction treatment is critical for improving long-term recovery outcomes. Integrated treatment programs that address both mental health and addiction are crucial for breaking the cycle of substance use and mental health issues.
Social and Economic Factors
Socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and living conditions all contribute to the prevalence of addiction. People who are facing financial hardship, unemployment, or homelessness may be more likely to engage in substance use as a coping mechanism. Additionally, those with limited access to treatment options may struggle to find help for their addiction.
Living in poverty, facing unemployment, or experiencing unstable housing conditions can lead to stress and trauma that may fuel addiction. Communities that lack access to healthcare and mental health services are also more vulnerable to high rates of substance abuse.
The Consequences of Drug Addiction
Physical and Mental Health Effects
Addiction can have severe long-term effects on both physical and mental health. Some of the health issues associated with addiction include:
- Liver disease (alcohol addiction)
- Cardiovascular problems (drug use like cocaine and methamphetamine)
- Respiratory failure (opioid overdose)
- Cognitive impairments (long-term substance abuse)
- Mental health disorders (depression, anxiety, paranoia)
Addiction can lead to a range of chronic diseases, including liver cirrhosis, heart disease, lung disease, and neurological damage. The damage is not limited to the individual using the drugs; family members and communities often bear the brunt of the social and emotional consequences of addiction.
Additionally, addiction often results in significant emotional distress, leading to problems with relationships, work, and overall quality of life. The stigma surrounding addiction can also prevent individuals from seeking help, further exacerbating the problem.
Legal and Financial Impacts
Substance use disorder can lead to legal issues, including arrests, incarceration, and fines. It may also lead to financial instability as individuals may prioritize spending on drugs over necessities like housing, food, and healthcare. The financial burden of addiction can be overwhelming, leading to cycles of poverty and criminality.
Drug-related crimes, including drug trafficking and possession, can result in criminal charges that carry long-lasting consequences. The legal consequences of drug addiction can further perpetuate the cycle of addiction and instability.
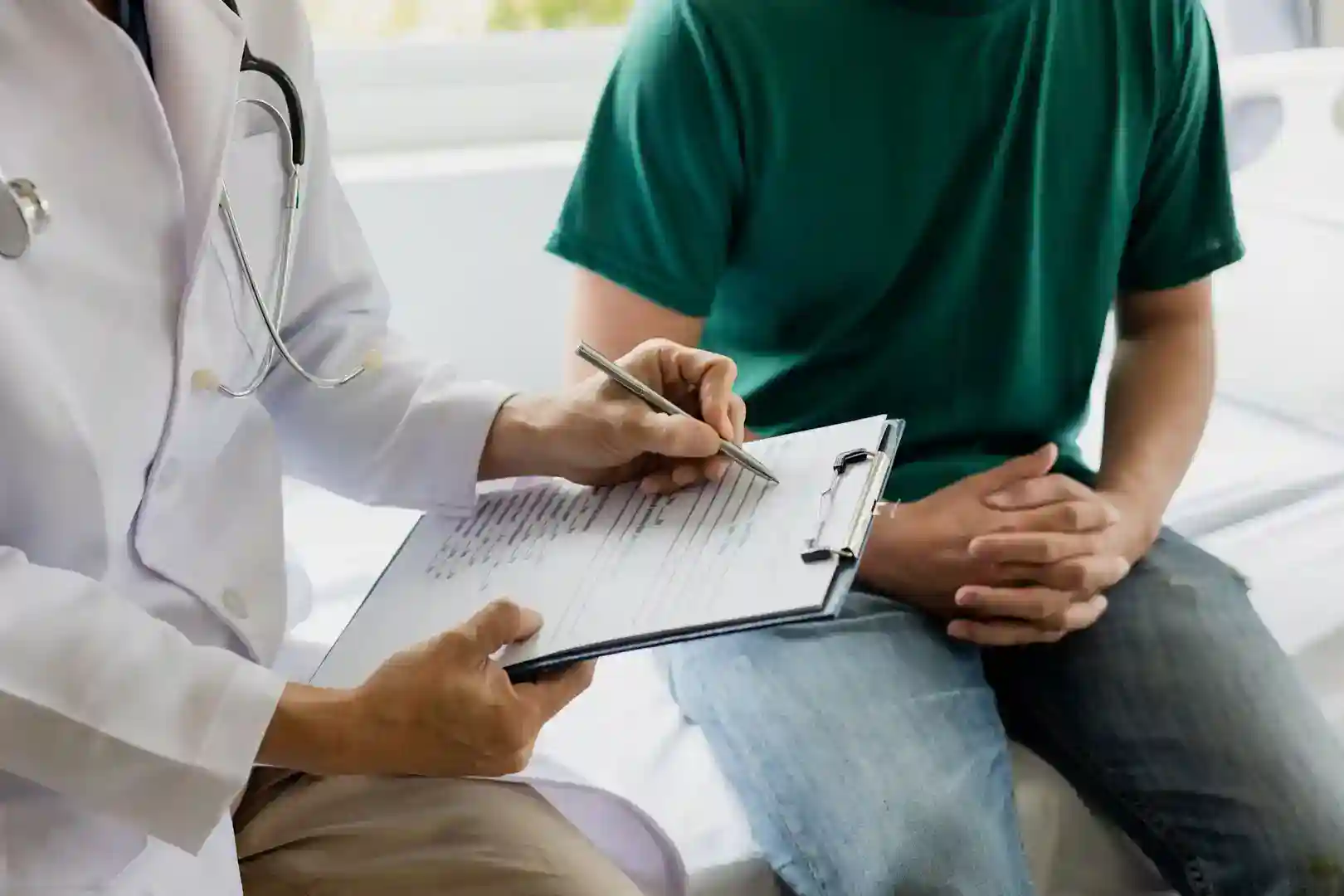
Treatment and Prevention of Drug Addiction
Treatment Options
Treatment for drug addiction involves a multi-faceted approach, which may include:
- Detoxification: The first step in recovery, which helps individuals safely withdraw from drugs under medical supervision. Detoxification can help individuals manage withdrawal symptoms and prepare for the next stages of treatment.
- Therapy and Counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and other therapeutic interventions can help individuals address the psychological aspects of addiction. Therapy provides tools for managing triggers, emotional regulation, and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): MAT involves using medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. MAT can be especially helpful for those recovering from opioid addiction.
- Support Groups: Groups like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) and Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) provide peer support and accountability for those in recovery. These groups are an essential component of long-term recovery, as they foster a sense of community and belonging.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing drug addiction requires a combination of education, early intervention, and access to treatment. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Public education campaigns about the dangers of substance use. These campaigns can help individuals understand the risks of drug use and the potential for addiction.
- School-based programs that teach students about healthy coping mechanisms. Providing youth with the tools to manage stress and emotional challenges can help reduce the likelihood of substance use.
- Access to mental health services to address underlying conditions that contribute to substance abuse. Providing access to therapy, counseling, and psychiatric care is vital in reducing addiction rates.
Conclusion
Drug addiction remains a significant public health crisis in the United States, affecting millions of individuals and their families each year. With over 46 million people suffering from a substance use disorder, the impact of addiction is vast and touches many areas of society. However, through proper treatment, prevention, and support, individuals can overcome addiction and lead fulfilling, drug-free lives.
If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, it’s important to reach out for help. Early intervention and treatment can significantly improve the chances of recovery.
Call Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606 for assistance and treatment options.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, don’t wait. Reach out to Addiction Helpline America today at (844) 561-0606.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
How many people in the U.S. are addicted to drugs?
What are the most commonly abused drugs in the U.S.?
How does drug addiction affect individuals and families?
What treatment options are available for drug addiction?
How can drug addiction be prevented?
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.