Introduction
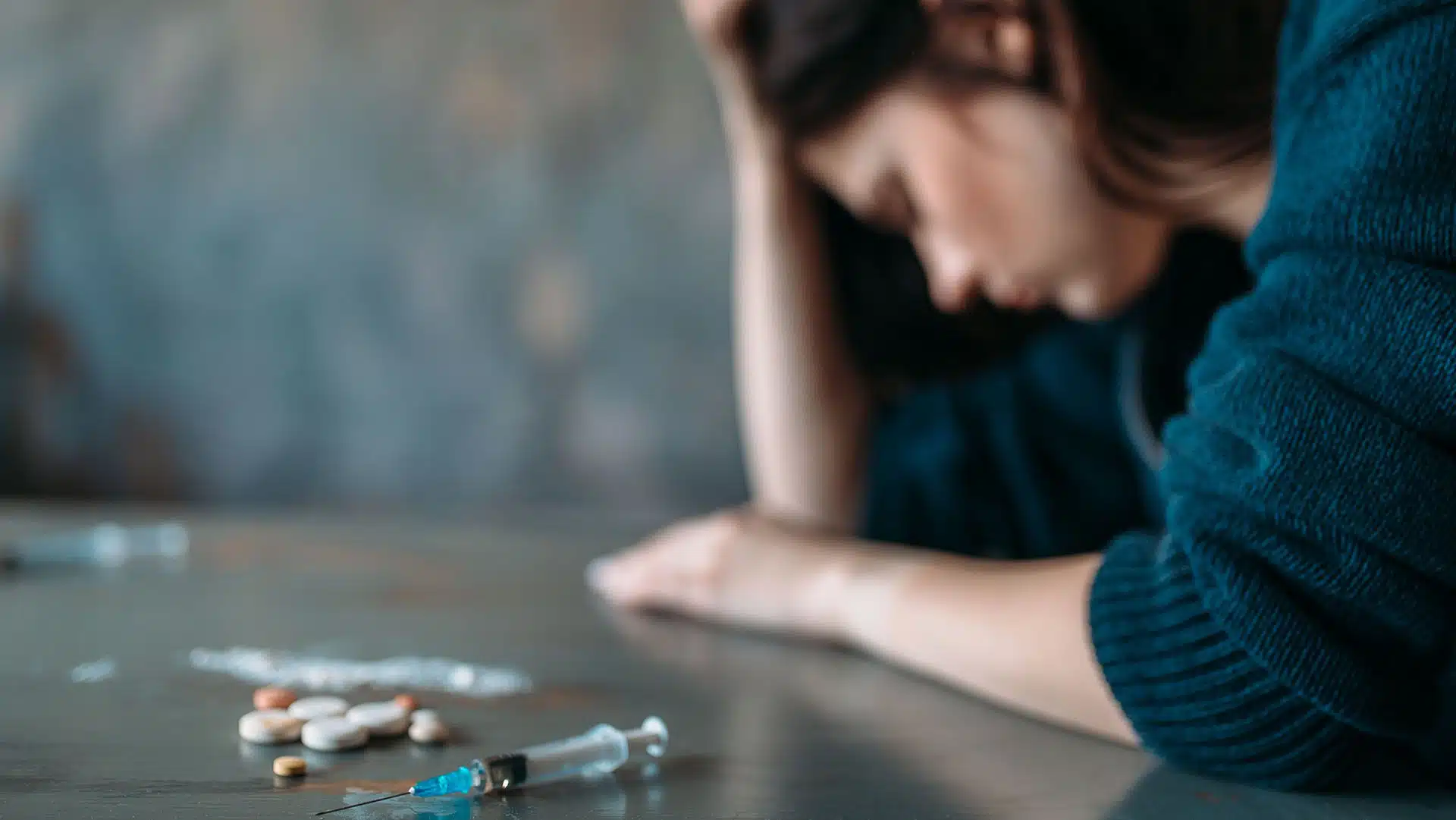
Drug addiction is a complex and widespread issue that affects millions of people around the world. It can destroy lives, families, and communities, yet many wonder what drives individuals to start using drugs and, ultimately, to become addicted. While there is no single reason why people get addicted to drugs, a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors plays a role in the development of addiction.
This article explores the various reasons behind drug addiction, including the impact of genetics, mental health, environment, and life experiences. By understanding why people become addicted to drugs, we can better address prevention, treatment, and recovery.
What Is Drug Addiction?
Definition of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction, also known as substance use disorder (SUD), is a chronic disease characterized by the compulsive use of drugs despite harmful consequences. Addiction alters brain function and behavior, leading to the inability to control drug use, cravings, and the prioritization of drugs over other aspects of life, such as relationships, work, and health.
Addiction is not a sign of moral weakness or lack of willpower. It is a medical condition that requires treatment and support. The process of becoming addicted is complex, often involving multiple contributing factors that increase the risk of developing a substance use disorder.
Biological Factors Behind Addiction
Genetics and Family History
Research suggests that genetics plays a significant role in the risk of developing addiction. If someone has a family history of addiction, they are more likely to struggle with substance use themselves. Genes can influence how an individual’s brain responds to drugs, making them more or less vulnerable to addiction.
Certain genetic factors can affect the way the body processes drugs, how the brain responds to rewards, and the likelihood of developing tolerance and dependence on substances. This genetic predisposition doesn’t guarantee addiction but increases the risk, particularly when combined with other factors like environmental stress or early exposure to drugs.
Brain Chemistry and Reward System
Drugs impact the brain’s reward system by releasing chemicals like dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins, which are responsible for feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. Many drugs, such as cocaine, opioids, and alcohol, cause an immediate rush of these “feel-good” chemicals, leading individuals to crave the positive sensation.
With repeated use, the brain adapts by altering its chemistry, which can lead to tolerance (requiring more of the substance to achieve the same effect) and dependence. Over time, these changes can reinforce drug-seeking behavior, making it harder to stop using drugs despite negative consequences.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Psychological Factors Behind Addiction
Mental Health Disorders
Many individuals who struggle with addiction also have underlying mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, or PTSD. People may turn to drugs as a way to self-medicate, attempting to cope with emotional pain or distress. However, this often exacerbates the issue, leading to a cycle of substance abuse and mental health challenges.
The connection between mental health and addiction is bidirectional—substance abuse can worsen mental health conditions, and mental health issues can increase the risk of turning to drugs as a coping mechanism. Treating both the addiction and the underlying mental health disorder is crucial for effective recovery.
Trauma and Stress
Traumatic experiences, especially in childhood, can significantly increase the risk of addiction. Abuse, neglect, and other forms of trauma can lead to emotional scars that may prompt individuals to seek relief through substance use. Similarly, ongoing stress, such as financial difficulties, relationship problems, or work-related stress, can drive people to use drugs to escape or numb their feelings.
Drugs can temporarily alleviate stress or pain, creating a cycle where individuals continue to use substances to cope with their challenges. Over time, this coping mechanism can become habitual, leading to addiction.
Environmental and Social Factors
Peer Pressure and Social Influence
Peer pressure is one of the most common reasons people, especially adolescents, start using drugs. In social situations, individuals may be influenced by friends or family members who use drugs or view substance use as acceptable. This social environment can normalize drug use and make it seem less risky, leading to experimentation and potential addiction.
As individuals continue to use drugs in social settings, they may develop a pattern of drug-seeking behavior, particularly if their social circles reinforce this behavior. Over time, this can lead to a deeper reliance on substances.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Availability and Accessibility of Drugs
The availability and accessibility of drugs in a person’s environment also play a significant role in the likelihood of addiction. If drugs are easy to obtain, whether through illegal means or prescription misuse, individuals may be more inclined to experiment or use substances regularly. Easy access to substances can normalize their use, increasing the risk of addiction.
Additionally, individuals living in environments with high levels of drug availability, such as neighborhoods with high rates of drug trafficking, may be at higher risk of becoming involved in substance use and addiction.
Family Dynamics and Childhood Environment
A person’s childhood environment can have a profound impact on their risk of addiction later in life. Children raised in households where drug use is prevalent, or where there is emotional neglect, abuse, or instability, are more likely to develop substance use problems.
Lack of parental supervision, support, and positive role models can increase a child’s exposure to drugs and foster risky behaviors that lead to addiction. On the other hand, a supportive family environment can provide protective factors that help prevent addiction.
The Cycle of Addiction
Tolerance and Dependence
As individuals continue using drugs, their bodies and brains develop tolerance, meaning they need more of the substance to achieve the same effects. This leads to increased drug use over time, which can escalate into dependence. Dependence occurs when the body becomes accustomed to the presence of the drug and experiences withdrawal symptoms when it’s not available.
Dependence creates a cycle where the individual uses drugs to avoid withdrawal symptoms, further reinforcing the addiction. This cycle can be difficult to break without proper treatment and support.
Addiction as a Compulsive Behavior
Addiction also manifests as a compulsive behavior, where individuals feel unable to control their drug use despite the negative impact it has on their lives. This compulsion is a result of changes in the brain’s reward system and prefrontal cortex, areas involved in decision-making, impulse control, and judgment.
As the addiction progresses, the individual’s focus shifts from other important aspects of life to obtaining and using drugs. The need to satisfy cravings overrides rational thought, leading to repeated use and reinforcing the addiction.
Treatment and Recovery
Addressing the Root Causes of Addiction
Effective treatment for drug addiction involves addressing the root causes, such as mental health issues, trauma, or environmental factors. Comprehensive treatment programs that combine therapy, counseling, and support groups can help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms, reduce cravings, and rebuild their lives.
Medically-assisted treatment may also be necessary for those dealing with withdrawal symptoms and dependence. These programs provide a safe and controlled environment to manage symptoms and support long-term recovery.
Support and Aftercare
Long-term recovery from addiction often requires ongoing support and aftercare. Family therapy, individual counseling, and community support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous, can provide the continued assistance needed to stay drug-free and build a fulfilling life.
Call Now – Your Journey to Recovery Begins Today!

Take the first step towards a healthier life! Call now to connect with our compassionate team and start your recovery journey today. Your path to healing awaits!
Our recovery specialists are available 24/7 to provide support, and all calls are confidential and free. Reach out anytime – we’re here to help!
Conclusion
People become addicted to drugs for a variety of reasons, including biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Genetics, brain chemistry, mental health issues, trauma, and social influences all contribute to the development of addiction. Understanding these factors is essential for prevention, treatment, and long-term recovery.
If you or someone you know is struggling with drug addiction, seeking help is the first step toward a healthier life. Treatment is available, and with the right support, recovery is possible.
Need Help with Addiction?
If you or someone you love is struggling with substance abuse, call Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606 for confidential support and treatment options.
What is the difference between drug addiction and drug dependence?
Can someone develop an addiction to drugs without any previous history of substance use?
What are the most common drugs that people get addicted to?
Can addiction be prevented?
What are the signs that someone may be struggling with addiction?
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.