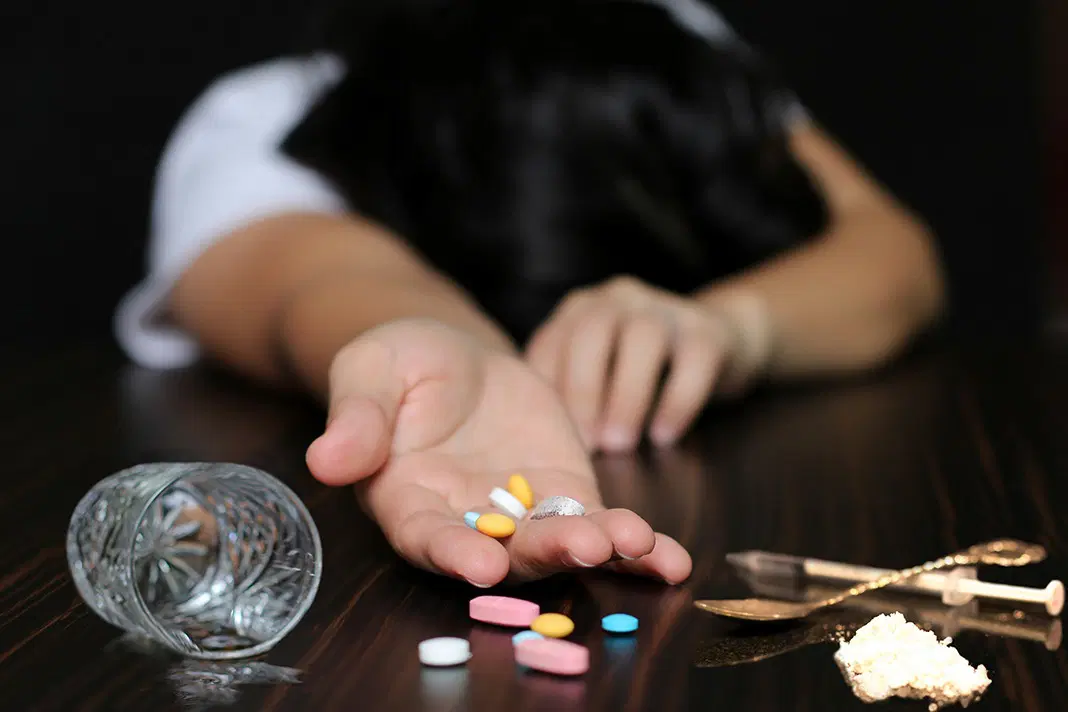
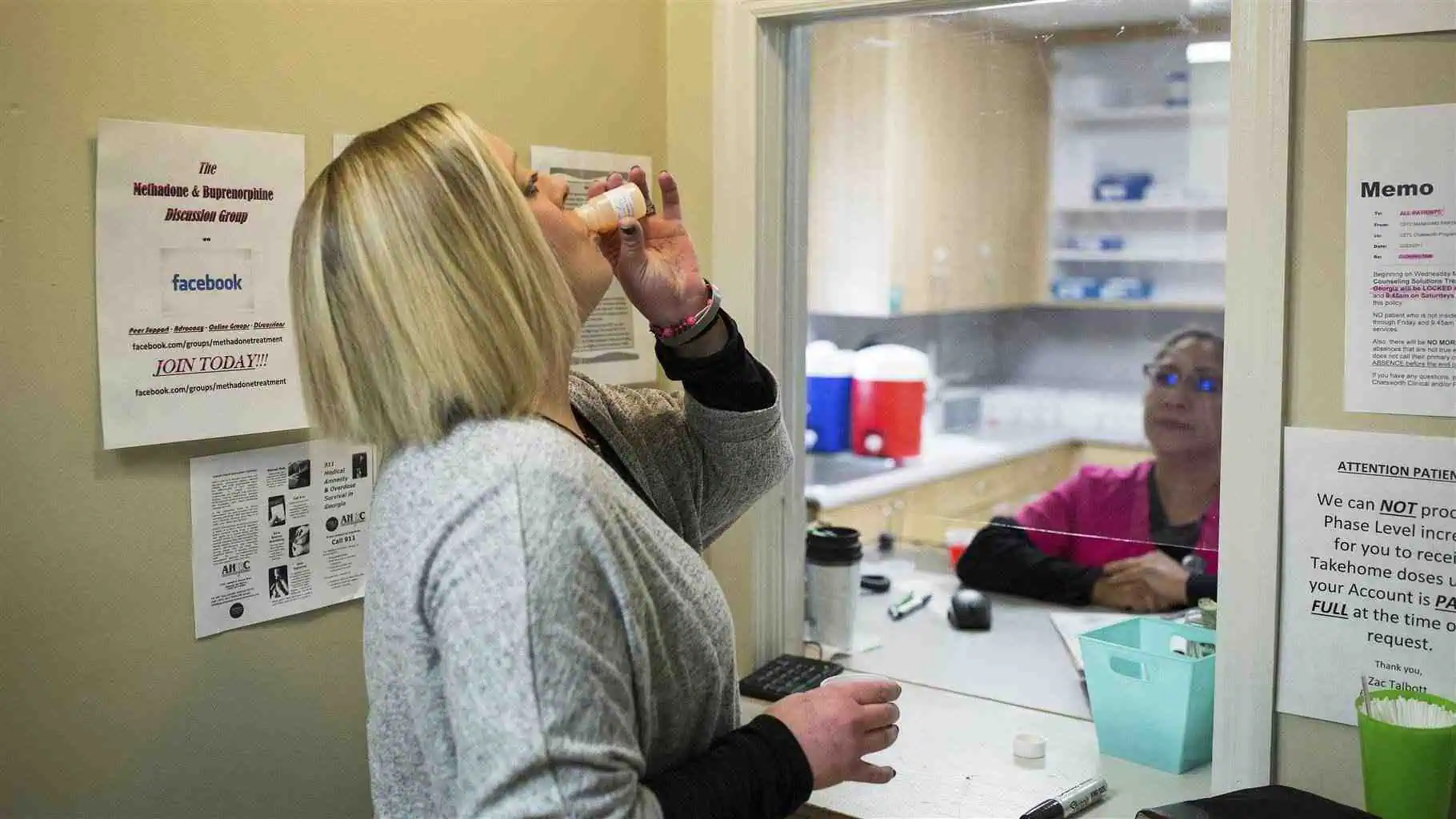
Drug usage has become a significant public health concern in recent decades. With the increase in the availability of both prescription and illicit substances, many are left wondering if the growing consumption of drugs is leading to a rise in addiction. Addiction is a complex condition that affects individuals physically, mentally, and socially. It is driven by many factors, and the usage of drugs is one of the leading causes. This article will explore the link between drug usage and addiction, the contributing factors, the effects of drug addiction, and how society can address this issue.
What is Addiction?
Before we dive into the impact of drug usage on addiction, it’s essential to understand what addiction is. Addiction is a chronic disorder that leads to the compulsive use of substances despite their harmful consequences. It often causes significant disruptions in an individual’s life, including physical health, mental well-being, relationships, and financial stability.
Addiction primarily affects the brain’s reward system, causing it to become reliant on certain substances for pleasure or relief. Over time, tolerance builds, meaning a person requires more of the substance to achieve the same effects. This leads to physical and psychological dependence.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
How Addiction Affects the Brain
- Altered Neurotransmitter Function: Drug use impacts neurotransmitters, chemicals that help transmit messages between nerve cells. This is particularly evident with substances like opioids, alcohol, and stimulants, which affect dopamine (the pleasure neurotransmitter).
- Changes in Brain Structure: Long-term drug use can cause changes in the brain’s structure, particularly in areas responsible for decision-making, memory, and self-control. This makes quitting the drug more difficult.
- Increased Reward Sensitivity: Drugs activate the brain’s reward pathways, leading to pleasurable feelings that reinforce the behavior and make the user seek out the drug repeatedly.
The Connection Between Drug Usage and Addiction
The usage of drugs has risen significantly over the years, and this surge is directly linked to the increase in addiction rates. The usage of drugs leads many individuals to begin experimenting for various reasons, and this initial use can quickly escalate to addiction. Let’s break down the major contributing factors to this link.
1. The Growing Availability of Drugs
In today’s society, drugs are more accessible than ever before. Whether through street dealers, prescription medications, or online marketplaces, drugs are easier to acquire.
- Prescription Medications: Prescription drugs, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and stimulants, have been a primary source of addiction. Many people initially use these drugs for legitimate medical purposes, but misuse leads to dependence.
- Illicit Drugs: The widespread availability of illicit drugs like marijuana, cocaine, methamphetamines, and synthetic drugs increases the chances of addiction, especially among young adults and adolescents.
2. The Role of Prescription Drug Abuse
Prescription drug abuse has played a central role in the rise of addiction in the United States and other countries. Opioids, in particular, have been the subject of a national crisis due to their highly addictive nature.
- Over-Prescription: For years, doctors prescribed painkillers like OxyContin and Percocet without fully considering the long-term consequences of their use. This led to an epidemic of opioid addiction.
- Misuse of Prescription Drugs: Many individuals misuse prescription drugs by taking them in higher doses than prescribed, or using them for recreational purposes. This misuse is a direct contributor to addiction.
3. The Impact of Mental Health Issues
Drug addiction is often interlinked with mental health issues. Many individuals use drugs as a form of self-medication to cope with stress, anxiety, depression, trauma, or other mental health disorders.
- Co-occurring Disorders: Mental health disorders and substance use disorders frequently occur together, making addiction more challenging to treat. Drugs can temporarily mask the symptoms of mental health problems, but over time, they can make the situation worse.
- Increased Vulnerability: People with mental health challenges are more likely to turn to substances to manage their emotions or pain. This creates a higher risk for addiction.
4. Social and Environmental Factors
Certain social and environmental factors make individuals more vulnerable to drug addiction. These factors can include:
- Peer Pressure: Adolescents and young adults, in particular, may be influenced by their social circles to try drugs. Peer pressure and a desire for social acceptance can play a significant role in initiating drug use.
- Family History of Addiction: A family history of substance use disorders increases an individual’s likelihood of developing addiction themselves. Genetics play a role in how people respond to drugs, making some more susceptible to addiction.
- Socioeconomic Status: People from lower-income backgrounds may be at a higher risk of addiction. Poverty, lack of education, and limited access to mental health services can contribute to substance abuse.
- Living in High-Risk Environments: In communities where drug use is normalized or glamorized, individuals are more likely to experiment with drugs and eventually develop an addiction.
The Consequences of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction can have devastating effects on the person using the substances, their loved ones, and society at large. Here are some of the key consequences of drug addiction:
1. Health Consequences
Long-term drug use can cause a variety of physical and mental health issues. These include:
- Liver and Kidney Damage: Many drugs, such as alcohol and certain opioids, can cause severe damage to the liver and kidneys.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Drugs like cocaine and methamphetamines can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Neurological Damage: Prolonged drug use can result in brain damage, memory loss, and cognitive impairment.
- Mental Health Decline: Addiction often exacerbates mental health issues, leading to depression, anxiety, paranoia, and suicidal thoughts.
2. Social and Relationship Problems
Addiction can severely impact an individual’s relationships with family, friends, and colleagues.
- Strained Family Dynamics: Family members often experience emotional distress due to the behavior of an addicted loved one. Marriages and familial bonds can deteriorate.
- Social Isolation: Many people struggling with addiction withdraw from social circles due to guilt, shame, or fear of judgment. This isolation can perpetuate the cycle of addiction.
- Loss of Employment: Addiction often affects job performance, leading to job loss or difficulty maintaining employment.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
3. Financial Burden
The financial costs of addiction can be staggering, both for individuals and society.
- Personal Finances: Individuals may spend large amounts of money to fund their drug habit, leading to financial instability, debt, and homelessness.
- Healthcare Costs: The healthcare system bears a significant financial burden due to drug-related health issues, including hospitalizations and addiction treatment.
4. Crime and Legal Problems
Addiction is often linked to criminal behavior, whether through theft, drug trafficking, or other illegal activities.
- Increased Crime Rates: Many individuals with addictions resort to crime to support their drug habits. This contributes to higher crime rates in certain areas.
- Legal Issues: Drug use and possession can lead to arrests, convictions, and long-term legal consequences.
Statistics on Drug Use and Addiction
National and Global Statistics
- United States: According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), more than 19 million Americans aged 12 or older struggled with a substance use disorder in 2020.
- Global Trends: The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) reports that around 275 million people worldwide have used drugs, and millions are at risk of addiction.
- The Opioid Crisis: The U.S. has seen more than 50,000 opioid-related overdose deaths in 2019 alone, illustrating the scale of the opioid epidemic.
State and Local Data
- High-Risk States: California, Florida, and Texas have reported some of the highest rates of drug abuse and addiction-related deaths.
- Urban Areas: New York City and Philadelphia have seen increases in drug-related crimes and overdose fatalities due to the availability of opioids and synthetic drugs.
- Emerging Trends: Areas like Washington, D.C. have raised concerns about PCP-laced marijuana, a growing issue in urban communities.
Addressing the Rise in Addiction
1. Prevention Programs
The key to addressing rising addiction rates lies in prevention. Education about the dangers of drug use and the signs of addiction can deter individuals from experimenting with drugs.
- School Programs: Early prevention education in schools helps deter young people from using drugs.
- Community Outreach: Programs in communities can raise awareness and provide resources for families to address drug use early.
2. Early Intervention
Detecting signs of addiction early can prevent further escalation. Healthcare professionals and social workers can play an essential role in identifying early drug use and providing support.
3. Effective Treatment Options
Treatment for addiction is available, and various approaches are used to help individuals recover.
- Medical Detox: Medical supervision during withdrawal helps manage dangerous symptoms.
- Therapy and Counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing, and other forms of therapy are effective in treating addiction.
- Support Groups: Programs like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide ongoing support for recovery.
4. Long-Term Recovery Support
Recovery is a long-term process, and individuals need ongoing support to maintain sobriety. Aftercare programs, sober living homes, and continuing therapy are essential for sustained recovery.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Conclusion
The increase in drug usage is undeniably contributing to the rise in addiction rates. As drugs become more accessible, individuals are more likely to experiment with substances, often leading to addiction. The consequences of addiction are profound, affecting individuals’ health, relationships, finances, and even society as a whole.
However, with early intervention, effective treatment, and long-term support, recovery is possible. It is crucial that we invest in prevention, education, and access to care to address the growing addiction crisis.
If you or someone you know is struggling with drug addiction, seeking professional help is the first step toward recovery. Contact Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606 to find the best treatment options available.
Is drug use always a sign of addiction?
What are the main signs of drug addiction?
Increased tolerance: Needing more of the substance to achieve the same effects.
Compulsive behavior: Using drugs despite knowing the risks and consequences.
Physical and psychological changes: Neglecting responsibilities, changes in appearance, and emotional instability.
Withdrawal symptoms: Experiencing physical or psychological discomfort when not using the substance.
Loss of control: Difficulty stopping drug use even when it negatively affects one’s life.
What types of drugs are most commonly abused?
Opioids: Prescription painkillers (e.g., OxyContin, Vicodin), heroin.
Stimulants: Cocaine, methamphetamines, and prescription stimulants (e.g., Adderall).
Depressants: Benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium) and alcohol.
Cannabis: Marijuana, particularly with increased potency.
Hallucinogens: LSD, PCP, and ecstasy. The abuse of these drugs is linked to both physical dependence and the development of addiction.
How does drug addiction affect the brain?
How can I help a loved one struggling with addiction?
Encourage them to seek professional help: Suggest contacting addiction specialists or visiting a treatment center.
Offer emotional support: Be compassionate and nonjudgmental.
Avoid enabling behaviors: Do not give them money or help them continue harmful habits.
Participate in family therapy: Support groups and therapy can help family members cope and provide guidance for intervention.
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.