Phencyclidine (PCP), commonly known as “angel dust,” is a dangerous hallucinogenic drug that alters brain function and can lead to severe psychological, and physical effects, and mental health disorders. Originally developed as an anesthetic, it was discontinued due to its serious side effects. Despite its classification as a Schedule II controlled substance, PCP remains a drug of abuse, with many users experiencing addiction and dependence. This raises the question: Is the PCP drug addictive?
This article explores whether the PCP drug is addictive, its symptoms, withdrawal effects, and treatment options.
Understanding PCP (Phencyclidine)
PCP is a synthetic dissociative drug that causes users to feel detached from reality. It affects neurotransmitter activity in the brain, leading to hallucinations, euphoria, aggression, and unpredictable behavior. While PCP was initially developed in the 1950s as an anesthetic for medical procedures, it was pulled from the market in the 1960s due to its dangerous side effects, such as agitation, delirium, and severe hallucinations. Despite its medical discontinuation, PCP became a popular recreational drug in the 1970s and has remained in circulation ever since.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
How PCP is Used
PCP is consumed in various ways, each affecting the body differently:
- Smoking – PCP is often mixed with marijuana or tobacco and smoked. Smoking it produces rapid effects and is one of the most common methods of abuse.
- Snorting – The powdered form of PCP is inhaled through the nose. This method also leads to quick intoxication and is highly dangerous.
- Injecting – Direct injection into the bloodstream results in immediate and intense effects. This method of use significantly increases the risk of overdose.
- Oral consumption – PCP can be ingested as a pill or dissolved in liquid, causing effects that last longer but are often more unpredictable.
Each method of use brings about different levels of intoxication, but all are dangerous and lead to serious health risks, especially with prolonged use.
How PCP Affects the Brain
PCP has a profound impact on the brain and body:
- Disrupts neurotransmitter function – PCP alters the way the brain communicates with the body by disrupting neurotransmitter activity, particularly those involving dopamine and glutamate. This disruption leads to cognitive impairments, altered sensations, and behavioral changes.
- Interferes with pain perception – Users often feel detached from their bodies, with reduced sensitivity to pain. This can lead to risky behavior, as they may not feel injuries or harm.
- Affects dopamine and serotonin levels – By manipulating the levels of these neurotransmitters, PCP can cause mood swings, aggression, and depression. The alteration of brain chemistry is a key factor in its addictive nature.
- Alters memory and coordination – Long-term use impairs memory, learning ability, and motor skills. Coordination issues increase the likelihood of accidents and physical harm.
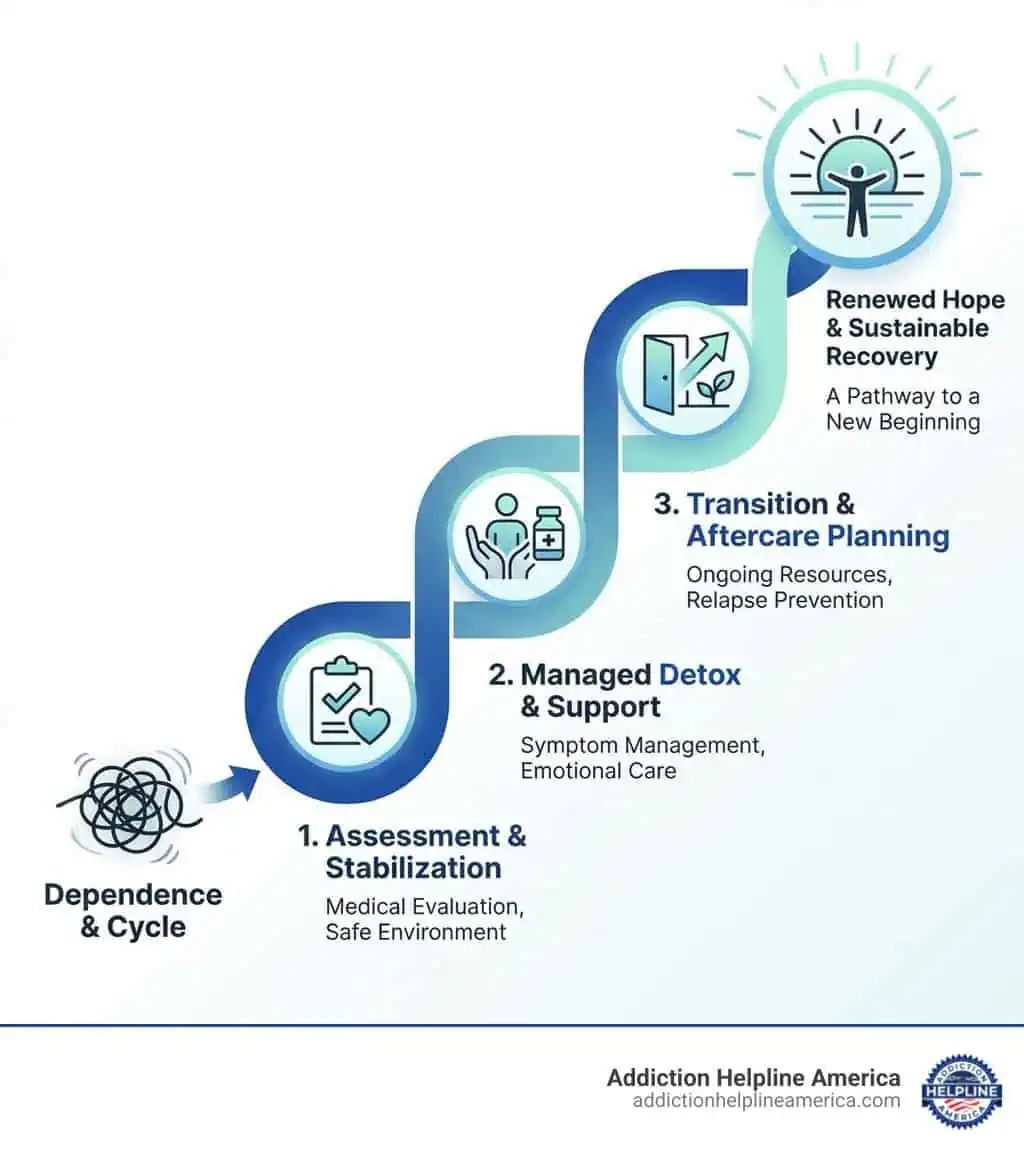
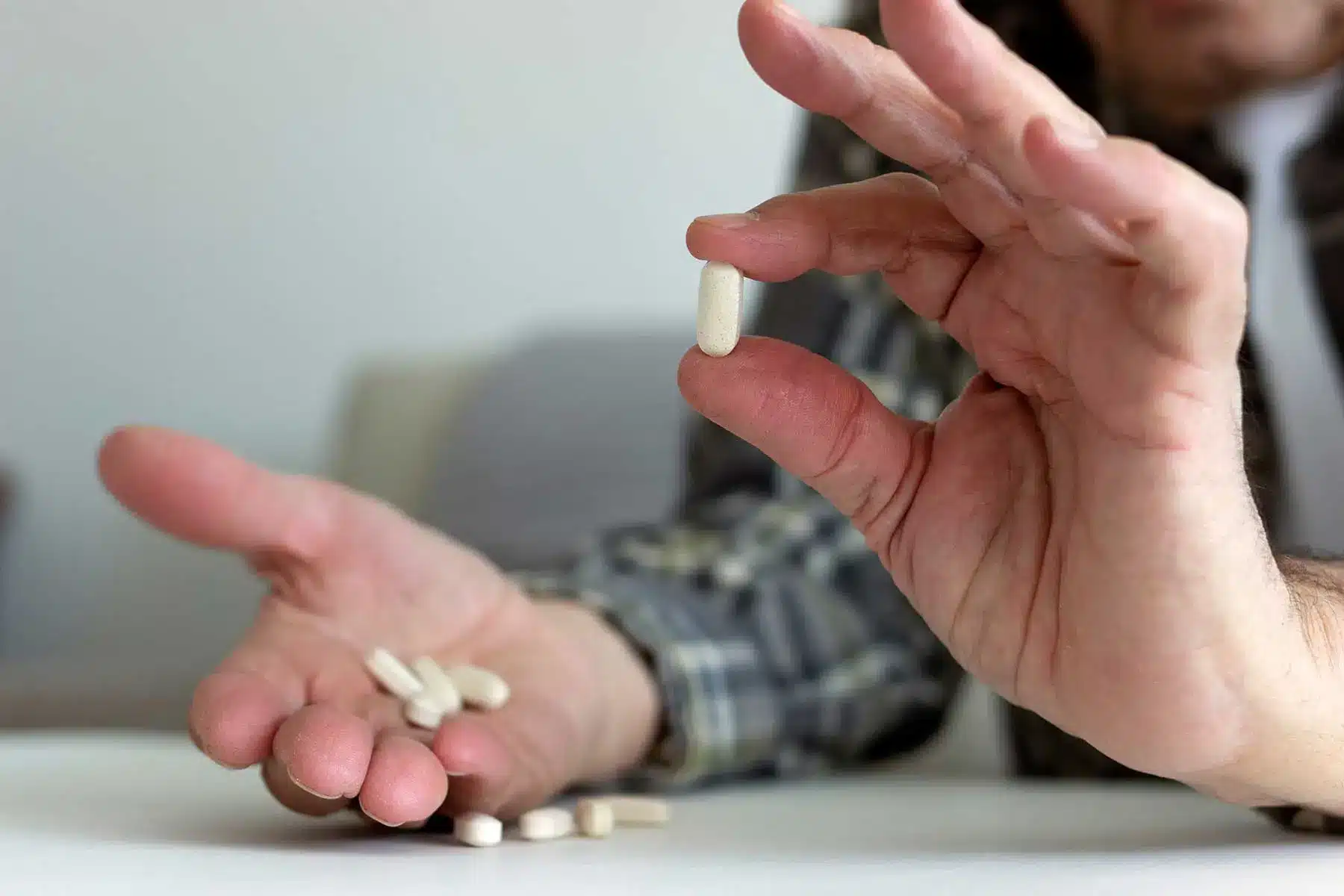
Is PCP Addictive?
Yes, PCP is highly addictive. While it may not create the same level of physical dependence as opioids, its psychological addiction can be just as severe. The strong dissociative effects and euphoria users experience when taking PCP can create a cycle of compulsive use, making it difficult for individuals to stop, even when they recognize the dangers.
Signs of PCP Addiction
PCP addiction is characterized by compulsive drug use and cravings. Key signs include:
- Increased tolerance – Users may require higher doses to achieve the same effects. Over time, tolerance builds, leading to escalating consumption.
- Compulsive drug use – Despite negative consequences, individuals may find it difficult to control their intake, using the drug in increasing quantities.
- Behavioral changes – Users may exhibit paranoia, aggression, and erratic behavior, including violent outbursts or emotional instability.
- Withdrawal symptoms – When users stop using PCP, they may experience intense discomfort, both physically and psychologically.
Why PCP is Addictive
Several factors contribute to PCP’s addictive nature:
- Strong psychological dependence – The dissociative and euphoric effects create a psychological craving that leads to compulsive use. Users may seek out the high as a means of escaping stress, anxiety, or emotional pain.
- Memory impairment – Long-term use of PCP leads to cognitive deficits, making it harder for individuals to break free from the cycle of abuse.
- Altered brain chemistry – PCP affects dopamine, which is responsible for reward and pleasure. This chemical change reinforces drug-seeking behavior, making addiction more likely.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Symptoms of PCP Use and Addiction
Short-Term Effects of PCP
PCP’s immediate effects can range from mild to life-threatening:
- Hallucinations and delusions – Users may see or hear things that aren’t real, creating an altered perception of reality.
- Euphoria and dissociation – A sense of detachment from reality, where users feel they are floating or outside of their body.
- Confusion and impaired judgment – This leads to poor decision-making, increasing the risk of accidents or dangerous behavior.
- Aggression and violent behavior – PCP can cause hostility, agitation, and violent outbursts, making individuals unpredictable and a risk to themselves and others.
- Loss of coordination and numbness – Users may feel detached from their own bodies and experience difficulty with motor control.
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate – Higher doses of PCP can lead to serious cardiovascular issues, including strokes and heart attacks.
Long-Term Effects of PCP
Chronic PCP use leads to serious mental and physical health problems, which can be irreversible:
- Persistent anxiety and paranoia – Long-term users often experience ongoing fear, distrust, and a heightened state of alertness.
- Memory loss and cognitive impairment – Prolonged use of PCP can cause permanent damage to memory, learning, and brain function.
- Speech difficulties and slurred speech – Communication problems arise as the brain’s cognitive functions deteriorate.
- Depression and suicidal thoughts – Mental health disorders, including depression and suicidal ideation, are common among chronic users.
- Organ damage – PCP is toxic to the body, causing damage to the kidneys, liver, and cardiovascular system.
PCP Withdrawal Symptoms
PCP withdrawal can be severe, especially for long-term users. Symptoms include both psychological and physical distress.
Common PCP Withdrawal Symptoms
- Depression and suicidal thoughts – The sudden shift in brain chemistry can lead to mood swings, depression, and suicidal ideation.
- Intense cravings for PCP – Users may experience overwhelming urges to use PCP again, even in the face of negative consequences.
- Anxiety and paranoia – Increased fear, restlessness, and agitation are common during withdrawal.
- Hallucinations and delusions – Some users continue to experience psychotic symptoms long after stopping the drug.
- Speech difficulties and confusion – Mental fog and confusion can make it hard to think clearly or communicate effectively.
- Muscle pain and tremors – Physical discomfort, including muscle aches and involuntary shaking, is common during withdrawal.
How Long Do PCP Withdrawal Symptoms Last?
- 24 hours after stopping – Initial withdrawal symptoms begin, often including cravings, irritability, and anxiety.
- 3–7 days – The acute withdrawal phase typically lasts 3 to 7 days, during which psychological symptoms like depression, anxiety, and hallucinations peak.
- Weeks to months – While the most intense symptoms fade, cravings, depression, and anxiety can persist for weeks or even months.
Treatment for PCP Addiction
Overcoming PCP addiction requires professional intervention, therapy, and long-term support.
Detox and Medical Supervision
The first step in treating PCP addiction is detoxification, which must be done under medical supervision. Medical detox ensures that withdrawal symptoms are managed safely, minimizing the risk of self-harm or severe psychological distress.
- Medications may be prescribed to address symptoms of psychosis, anxiety, or depression during detox.
- Supervised care is essential to ensure safety during the withdrawal process.
Therapy and Behavioral Treatments
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) – This therapy helps individuals identify and change patterns of behavior that contribute to drug use, providing tools for managing cravings and stress.
- Motivational therapy – Encourages individuals to commit to recovery by helping them build motivation to change their behavior.
- Support groups – Groups like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide peer support, accountability, and shared experiences, which can be crucial for recovery.
Rehabilitation Programs
- Inpatient rehab – This option provides 24/7 medical and psychological care in a controlled environment, ideal for individuals with severe addiction.
- Outpatient treatment – For those with less severe addiction, outpatient programs allow individuals to receive treatment while continuing to live at home.
- Dual diagnosis programs – These programs treat both addiction and co-occurring mental health conditions, ensuring a more comprehensive approach to recovery.
PCP Abuse Statistics in the U.S.
PCP use is less common than opioids or stimulants but remains a public health concern. Key PCP statistics include:
- 6 million people in the U.S. have tried PCP at least once.
- PCP-related emergency room visits increased by 400% between 2005 and 2011.
- Young adults (ages 18-25) are the most likely to use PCP.
- PCP-related arrests have risen in major cities.
- High school students report experimenting with PCP, though usage rates are lower than in the 1990s.
State and City-Specific PCP Use Data
- California, Texas, and Florida report the highest PCP-related hospitalizations.
- Philadelphia and New York City have seen an increase in PCP-related crimes.
- Washington, D.C. has reported growing concerns about PCP-laced marijuana.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Get Help for PCP Addiction
PCP addiction is dangerous and life-threatening, but recovery is possible with the right support. Seeking treatment early increases the chances of successful recovery.
Call Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606 today to find the best treatment options.
Conclusion
PCP is a highly addictive and dangerous drug that can have devastating effects on both the mind and body. Its powerful ability to alter perception and cause intense psychological disturbances makes it a significant threat to those who use it. While the road to recovery can be challenging, it is important to remember that help is available. With proper treatment, including medical detox, therapy, and support systems like rehabilitation programs, individuals can overcome PCP addiction and regain control of their lives.
If you or someone you know is struggling with PCP addiction, reaching out for professional help is the first step toward recovery. The Addiction Helpline America is available at (844) 561-0606, offering resources and guidance to find the right treatment options. Don’t wait—take action today to begin the journey toward a healthier, drug-free life.
What is PCP, and how does it affect the body?
Is PCP addictive?
What are the withdrawal symptoms of PCP?
How is PCP addiction treated?
Can I recover from PCP addiction?
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.