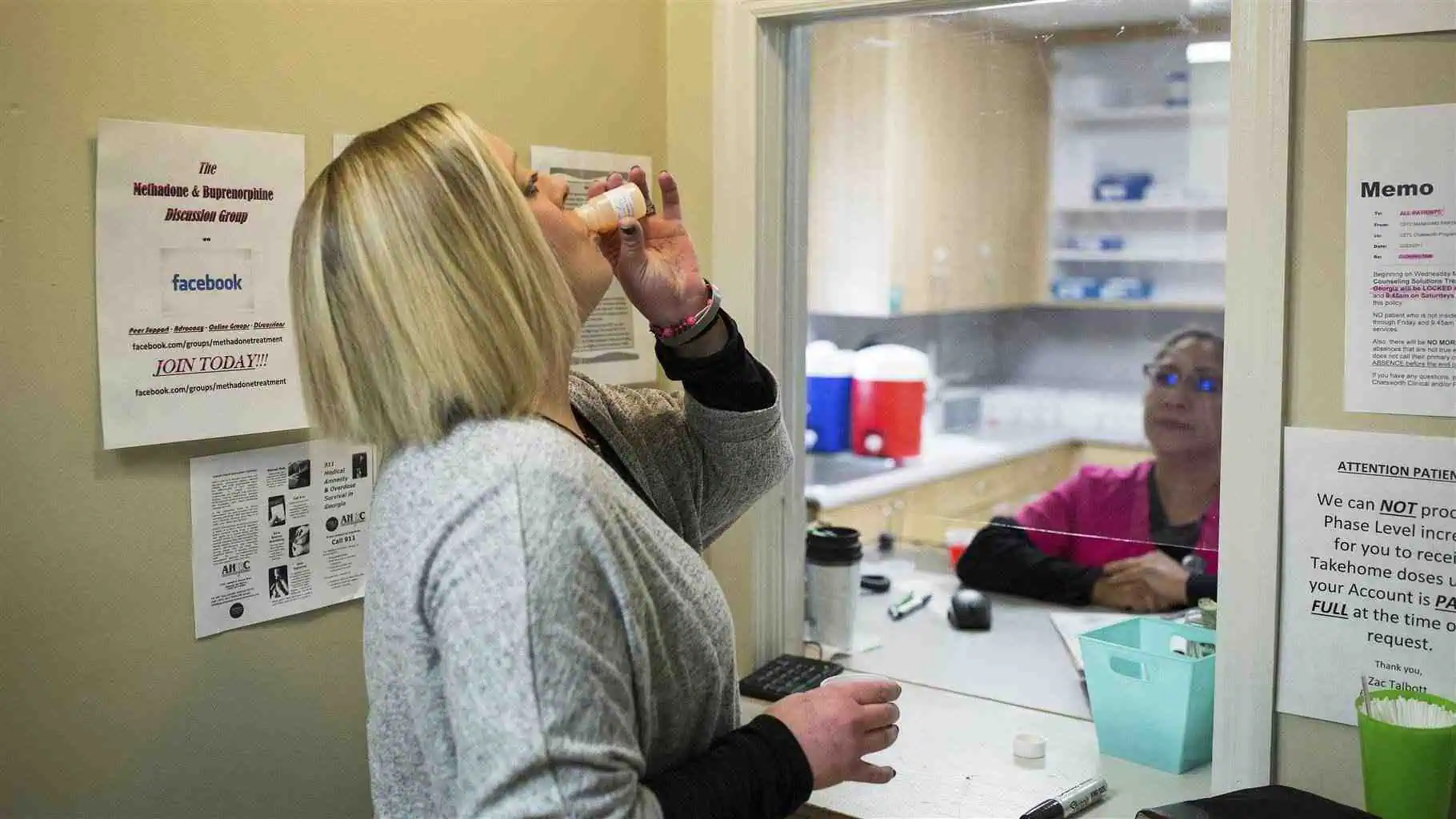
Introduction
When it comes to drug use, the risk of addiction is a major concern. While many drugs have the potential for abuse and dependency, there are some substances considered to have a low potential for addiction. Understanding which drugs are less likely to cause dependency can help individuals make informed choices, whether they are seeking medical treatment or simply curious about the safety of certain substances.
In this article, we will explore some of the most non-addictive drugs, their uses, and why they are considered low-risk. It’s important to note that even substances with a low addiction potential can be misused, leading to adverse effects. If you or a loved one is struggling with substance use issues, contact Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606 for support.
Understanding Drug Addiction and Dependency
What Is Addiction?
Addiction is a complex condition characterized by the inability to stop using a substance despite negative consequences. It affects both the brain and behavior and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Drugs that are highly addictive typically affect the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine or other chemicals that create feelings of euphoria. These substances can lead to compulsive use, where the person feels a constant urge to consume the drug to avoid negative feelings or withdrawal symptoms.
Addiction is often considered a chronic disease because it can last a long time and require ongoing treatment or intervention. While some people are able to manage their addiction with professional help, others may face significant challenges in maintaining sobriety.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
What Makes a Drug Addictive?
Certain drugs have a higher potential for addiction because they create intense feelings of pleasure or euphoria. Substances like heroin, cocaine, and alcohol can cause physical dependence, where the body adapts to the presence of the drug, leading to withdrawal symptoms when it is not available.
- Heroin: Heroin is known for its powerful euphoric effects and has a high risk of physical dependence. The withdrawal symptoms can be severe and include pain, nausea, and cravings.
- Cocaine: Cocaine stimulates the central nervous system, producing feelings of increased energy and euphoria. It can lead to both psychological and physical addiction, with symptoms like cravings and intense fatigue after the drug wears off.
- Alcohol: While legal, alcohol is one of the most commonly abused substances. It can lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms such as tremors, sweating, and even seizures in severe cases.
On the other hand, some drugs have milder effects on the brain’s reward system, and therefore, are less likely to lead to addiction. However, this does not mean they are completely risk-free, and misuse of even these substances can lead to negative consequences.
Most Non-Addictive Drugs
1. Psilocybin (Magic Mushrooms)
Psilocybin, the active compound in magic mushrooms, has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits, particularly for conditions like depression and anxiety. Research suggests that psilocybin is not physically addictive, and its potential for abuse is low compared to other substances.
- How It Works: Psilocybin affects serotonin receptors in the brain, leading to altered perceptions and emotional experiences. It can enhance feelings of connection and insight but typically does not create a need for repeated use.
- Addiction Potential: There is no evidence of physical dependency or withdrawal symptoms associated with psilocybin use. Studies have shown that it does not trigger the same cravings that substances like cocaine or alcohol do.
- Potential Risks: While psilocybin is considered non-addictive, it can cause intense psychological experiences that may be unsettling or disorienting for some individuals. There is also the risk of bad trips, which may cause lasting distress or exacerbate mental health conditions in vulnerable individuals.
- Therapeutic Potential: Recent research suggests that psilocybin could have therapeutic benefits for treating depression, PTSD, and addiction itself, making it a subject of interest in mental health treatment.
2. Cannabis (Marijuana)
Cannabis is one of the most widely used recreational drugs around the world. While it does have some potential for misuse, it is generally considered less addictive than other substances, such as alcohol or opioids.
- How It Works: Cannabis contains compounds like THC that interact with the brain’s cannabinoid receptors to produce a sense of relaxation and altered perception. THC can provide a calming effect, but it doesn’t usually create the overwhelming cravings that addictive drugs do.
- Addiction Potential: Studies show that only a small percentage of individuals who use marijuana develop a dependence. Withdrawal symptoms are typically mild, such as irritability and sleep disturbances. The risk of developing a cannabis use disorder is higher in individuals who start using it at a young age or who use it frequently.
- Potential Risks: While not physically addictive, cannabis use can impair cognitive function, especially in heavy or long-term users. Prolonged use has been linked to issues like memory problems, reduced attention span, and psychosis in vulnerable individuals.
- Legal and Social Considerations: Cannabis remains illegal in some regions, and its use can lead to legal complications. In places where it is legal, there are still ongoing discussions about its potential for abuse and its long-term effects on mental health.
3. Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic commonly used in medical settings. It is also sometimes used recreationally for its hallucinogenic effects. Although it has some potential for psychological dependence, ketamine is not physically addictive in the same way that other drugs like opioids or alcohol are.
- How It Works: Ketamine affects the brain’s NMDA receptors, leading to a sense of detachment from reality and, in some cases, hallucinations. It’s used in medical settings for anesthesia, particularly in surgical procedures and for treating severe pain.
- Addiction Potential: Ketamine has a low addiction potential, but psychological cravings can develop in frequent users. Unlike opioids or alcohol, ketamine does not cause significant physical withdrawal symptoms, which is why it is considered less addictive.
- Potential Risks: Prolonged use can lead to bladder problems, cognitive impairment, and psychological issues such as memory loss and dissociation. Ketamine use can also be dangerous in large doses and has been associated with emergency room visits due to accidents or psychological distress.
4. MDMA (Ecstasy)
MDMA is known for its stimulant and empathogenic properties, making it popular in social settings and among party-goers. It is often used for its mood-lifting effects, but the addiction potential is considered to be relatively low compared to substances like heroin or cocaine.
- How It Works: MDMA increases the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain, producing feelings of euphoria and empathy. The drug is typically taken in pill form and is popular in rave and party environments.
- Addiction Potential: Although MDMA can lead to psychological dependence, physical addiction is uncommon. Many users experience a “comedown” after use, which can lead to cravings for the drug. However, the craving is often more related to the emotional highs of the drug than to physical dependence.
- Potential Risks: Long-term use of MDMA can lead to serotonin depletion, which may cause mood disturbances, memory problems, and emotional exhaustion. Heavy use can also affect sleep patterns and overall brain function.
5. Dextromethorphan (DXM)
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is an ingredient commonly found in cough syrups. At high doses, it can cause hallucinations and dissociation, but when used in its proper dose, it is generally considered non-addictive.
- How It Works: DXM affects the brain’s NMDA receptors, similar to ketamine, creating a dissociative and hallucinogenic effect. At regular doses, it is used to treat coughs and cold symptoms.
- Addiction Potential: DXM has a low risk of addiction, though some individuals may misuse it recreationally, leading to psychological dependence. The physical withdrawal symptoms are minimal, but the psychological cravings can still occur with frequent misuse.
- Potential Risks: At high doses, DXM can cause serious side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and heart problems. Misuse can also result in dangerous interactions with other medications.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Why Are These Drugs Considered Non-Addictive?
1. Low Physical Dependency Risk
Most of the substances listed above do not cause the same level of physical dependence that drugs like heroin or alcohol do. Users may experience a psychological desire to use them, but withdrawal symptoms are generally mild or nonexistent. This lack of physical dependence is what sets these substances apart from highly addictive drugs.
2. Milder Effects on the Brain’s Reward System
Drugs with a low addiction potential often do not trigger the same intense release of dopamine or other “feel-good” chemicals in the brain. This means they don’t create the strong cravings or compulsive need that other drugs can cause. While they may provide temporary pleasure or altered perception, they don’t create the same reinforcing cycle of reward and craving that drives addiction.
3. Short-Term Effects
Many of these substances are short-acting and do not require frequent use to maintain their effects. For example, psilocybin and MDMA have relatively short durations of action, which makes regular misuse less likely. Their effects typically wear off within a few hours, reducing the potential for habitual use.
Can Non-Addictive Drugs Still Be Harmful?
While these drugs are generally considered non-addictive, misuse can still lead to adverse effects. For example:
- Psychological effects: Hallucinogens like psilocybin and MDMA can lead to psychological distress or trigger underlying mental health conditions, such as anxiety or paranoia.
- Cognitive impairment: Long-term use of certain substances, like ketamine or MDMA, can lead to memory problems and difficulty concentrating.
- Legal consequences: Even non-addictive drugs like cannabis are illegal in some places, and their use can lead to legal repercussions. Misusing substances like DXM can also result in legal issues due to their over-the-counter availability.
Find Hope and Healing: Call Us Now!
Take the first step towards a brighter future! If you or a loved one is seeking support for substance abuse, we are here to help. Call us today and let our dedicated team guide you to the right treatment options. Your path to recovery starts now!
- Connect with an expert addiction specialist 24/7/365
- Learn about treatment costs
- Arrange fast access to a treatment program
Request a Call
OR
Make a Call
Conclusion
While no drug is entirely free from risks, there are substances with a lower potential for addiction. Drugs like psilocybin, cannabis, ketamine, MDMA, and DXM are often considered non-addictive or low-risk for dependence. However, misuse of any substance can lead to unwanted effects, and even low-risk drugs should be used responsibly.
If you or someone you know is struggling with substance use or addiction, don’t hesitate to reach out to Addiction Helpline America at (844) 561-0606 for confidential support and guidance.
Are non-addictive drugs completely safe to use?
Can psilocybin (magic mushrooms) cause addiction?
Is cannabis (marijuana) addictive?
Can MDMA (ecstasy) lead to addiction?
What should I do if I feel like I’m becoming dependent on a non-addictive drug?
Our helpline is 100%
free & confidential
If you or someone you care about is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we can help you explore your recovery options. Don’t face this challenge alone—seek support from us.
Programs
Resources
Will my insurance
cover addiction
treatment?
We're ready to help
Find the best
drug or alcohol treatment
center
Are you or a loved one struggling with addiction? Call today to speak to a treatment expert.